The role of hepatic macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 30671098
- PMCID: PMC6333604
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.133
The role of hepatic macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
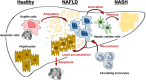
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is becoming common chronic liver disease because of the increasing global prevalence of obesity and consequently Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, the mechanism for progression of NAFLD to NASH and then cirrhosis is not completely understood, yet. The triggering of these hepatic diseases is thought from hepatocyte injury caused by over-accumulated lipid toxicity. Injured hepatocytes release damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which can stimulate the Kupffer cells (KCs), liver-resident macrophages, to release pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and recruit monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). The increased activation of KCs and recruitment of MDMs accelerate the progression of NAFLD to NASH and cirrhosis. Therefore, characterization for activation of hepatic macrophages, both KCs and MDMs, is a baseline to figure out the progression of hepatic diseases. The purpose of this review is to discuss the current understanding of mechanisms of NAFLD and NASH, mainly focusing on characterization and function of hepatic macrophages and suggests the regulators of hepatic macrophages as the therapeutic target in hepatic diseases.
Keywords: Kupffer cell; Macrophage; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: The authors declare that there is no financial conflict of interests to publish these results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Macrophage heterogeneity role in NAFLD and NASH disease progression].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023 Jul 20;31(7):770-775. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220428-00223. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37580264 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic inhibition of inflammatory monocyte recruitment reduces steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis.Hepatology. 2018 Apr;67(4):1270-1283. doi: 10.1002/hep.29544. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 28940700
-
Pathophysiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Clin Liver Dis. 2018 Feb;22(1):23-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Clin Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 29128059 Review.
-
Crosstalk Between Liver Macrophages and Surrounding Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 24;11:1169. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01169. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32670278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic transcriptome signatures in patients with varying degrees of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease compared with healthy normal-weight individuals.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Apr 1;316(4):G462-G472. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00358.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30653341
Cited by
-
Biocompatibility studies of fluorescent diamond particles-(NV)~800nm (part V): in vitro kinetics and in vivo localization in rat liver following long-term exposure.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Aug 12;14:6451-6464. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S209663. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31496697 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin Induces Apoptotic and Pyroptotic Cell Death via NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Rat Hepatocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12589. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212589. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830465 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrotrametenolic acid methyl ester, a triterpenoid of Poria cocos, alleviates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation via targeting Caspase-1 in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01569-9. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40329004
-
Inflammation/bioenergetics-associated neurodegenerative pathologies and concomitant diseases: a role of mitochondria targeted catalase and xanthophylls.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Feb;16(2):223-233. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.290878. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32859768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 3-week nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model shows elafibranor benefits on hepatic inflammation and cell death.Clin Transl Sci. 2020 May;13(3):529-538. doi: 10.1111/cts.12735. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Clin Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 31981449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998;114(4):842–845. - PubMed