Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes
- PMID: 30671100
- PMCID: PMC6333611
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.147
Mouse Cre-LoxP system: general principles to determine tissue-specific roles of target genes
Abstract
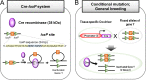
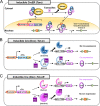
Genetically engineered mouse models are commonly preferred for studying the human disease due to genetic and pathophysiological similarities between mice and humans. In particular, Cre-loxP system is widely used as an integral experimental tool for generating the conditional. This system has enabled researchers to investigate genes of interest in a tissue/cell (spatial control) and/or time (temporal control) specific manner. A various tissue-specific Cre-driver mouse lines have been generated to date, and new Cre lines are still being developed. This review provides a brief overview of Cre-loxP system and a few commonly used promoters for expression of tissue-specific Cre recombinase. Also, we finally introduce some available links to the Web sites that provides detailed information about Cre mouse lines including their characterization.
Keywords: Cre portal sites; Cre-loxP system; tissue specific promoter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: The authors declare that there is no financial conflict of interests to publish these results.
Figures
References
-
- Nagy A. Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis. 2000;26(2):99–109. - PubMed
-
- Meinke G, Bohm A, Hauber J, Pisabarro MT, Buchholz F. Cre Recombinase and Other Tyrosine Recombinases. Chem Rev. 2016;116(20):12785–12820. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg N, Hamilton D. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. I. Recombination between loxP sites. J Mol Biol. 1981;150(4):467–486. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg N, Sauer B, Hoess R, Abremski K. Bacteriophage P1 cre gene and its regulatory region. Evidence for multiple promoters and for regulation by DNA methylation. J Mol Biol. 1986;187(2):197–212. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

