Growing pigs developed different types of diabetes induced by streptozotocin depending on their transcription factor 7-like 2 gene polymorphisms
- PMID: 30671104
- PMCID: PMC6333605
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.185
Growing pigs developed different types of diabetes induced by streptozotocin depending on their transcription factor 7-like 2 gene polymorphisms
Abstract
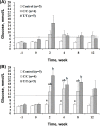
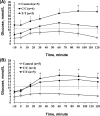
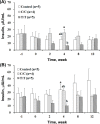
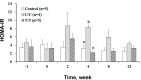
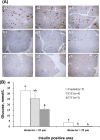
The different polymorphisms of the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene promote variances in diabetes susceptibility in humans. We investigated whether these genotypes also promote differences in diabetic susceptibility in commercial pigs. Growing pigs (Landrace, both sex, 50-60 kg) with the C/C (n=4) and T/T (n=5) TCF7L2 genotypes were identified and intravenously injected with streptozotocin (STZ, 40 mg/kg) twice in weekly intervals, then a high-energy diet was offered. Oral glucose tolerance tests, blood analyses and the homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index calculations were performed. The animals were sacrificed at the end of 12 weeks of treatment to reveal the pancreas histomorphometry. The results showed that all of the treated pigs grew normally despite exhibiting hyperglycemia at two weeks after the induction. The glycemic level of the fasting or postprandial pigs gradually returned to normal. The fasting insulin concentration was significantly decreased for the T/T carriers but not for the C/C carriers, and the resulting HOMA-IR index was significantly increased for the C/C genotype, indicating that the models of insulin dependence and resistance were respectively developed by T/T and C/C carriers. The histopathological results illustrated a significant reduction in the pancreas mass and insulin active sites, which suggested increased damage. The results obtained here could not be compared with previous studies because the TCF7L2 background has not been reported. Growing pigs may be an excellent model for diabetic in children if the animals are genetically pre-selected.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; growing pigs; high-energy diet; streptozotocin; transcription factor 7-like 2 genotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: The authors declare that there is no financial conflict of interests to publish these results.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. (2) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(Suppl 1):S8–S16. - PubMed
-
- Basile KJ, Guy VC, Schwartz S, Grant SF. Overlap of genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Curr Diab Rep. 2014;14(11):550. - PubMed
-
- Redondo MJ, Grant SF, Davis A, Greenbaum C T1D Exchange Biobank. Dissecting heterogeneity in paediatric Type 1 diabetes: association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 TT and low-risk human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes. Diabet Med. 2017;34(2):286–290. - PubMed
-
- Jin T. Current Understanding on Role of the Wnt Signaling Pathway Effector TCF7L2 in Glucose Homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2016;37(3):254–277. - PubMed

