In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacilllus paracasei HP7
- PMID: 30671108
- PMCID: PMC6333598
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.216
In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacilllus paracasei HP7
Abstract
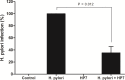
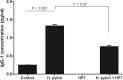
The efficacy of standard therapeutic strategies for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is decreasing over time due to the emergence of drug-resistant strains. As an alternative, the present study investigated the capacity of Lactobacilllus paracasei (L. paracasei) HP7, isolated from kimchi, to inhibit H. pylori growth. The effects of L. paracasei HP7 on H. pylori adhesion and H. pylori-induced inflammation were examined in AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma epithelial cells and a mouse model of H. pylori SS1 infection. L. paracasei HP7 reduced H. pylori adhesion to AGS cells and suppressed the inflammatory response in infected cells by downregulating interleukin-8. H. pylori colonization in the stomach of C57BL/6 mice was demonstrated by rapid urease test, and results showed significant decrease in mice post-treated with L. paracasei HP7. Additionally, L. paracasei HP7 decreased gastric inflammation and epithelial lesions in the stomach of H. pylori-infected mice. These results demonstrate that L. paracasei HP7 treatment can inhibit H. pylori growth and is thus a promising treatment for patients with gastric symptoms such as gastritis that are caused by H. pylori infection.
Keywords: AGS cells; HP7; Helicobacter pylori; Kimchi; Lactobacilllus paracasei.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: The authors declare that there is no financial conflict of interests to publish these results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of acomplex mixture of Lactobacillus paracasei HP7 including the extract of Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Glycyrrhiza glabra.Lab Anim Res. 2020 Oct 28;36:40. doi: 10.1186/s42826-020-00073-x. eCollection 2020. Lab Anim Res. 2020. PMID: 33134159 Free PMC article.
-
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei HP7 Improves Gastric Emptying by Modulating Digestive Factors in a Loperamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia Mouse Model.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 11;35:e2412035. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12035. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40081888 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Lp-115 inhibit Helicobacter pylori colonization and gastric inflammation in a murine model.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 9;13:1196084. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1196084. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37621875 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive and therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus paracasei ZFM54 on Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis by ameliorating inflammation and restoring gastric microbiota in mice model.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 24;9:972569. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.972569. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36091249 Free PMC article.
-
[Importance of Helicobacter pylori in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Experimental models in rodents].Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2000 Oct-Dec;65(4 Suppl 2):25-33. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2000. PMID: 11464619 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of acomplex mixture of Lactobacillus paracasei HP7 including the extract of Perilla frutescens var. acuta and Glycyrrhiza glabra.Lab Anim Res. 2020 Oct 28;36:40. doi: 10.1186/s42826-020-00073-x. eCollection 2020. Lab Anim Res. 2020. PMID: 33134159 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lactobacillus spp. on Helicobacter pylori: A Promising Frontier in the Era of Antibiotic Resistance.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Nov 5. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10396-z. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39499454 Review.
-
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei HP7 Improves Gastric Emptying by Modulating Digestive Factors in a Loperamide-Induced Functional Dyspepsia Mouse Model.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 11;35:e2412035. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12035. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40081888 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Dietary Patterns on H. pylori Infection and the Modulation of Microbiota to Counteract Its Effect. A Narrative Review.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 10;10(7):875. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070875. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34358024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990;161(4):626–633. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE. Recent developments in the epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2000;29(3):559–578. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama A, Maruta F, Ikeno T, Ishida K, Kawasaki S, Katsuyama T, Shimizu N, Tatematsu M. Helicobacter pylori infection enhances N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced stomach carcinogenesis in the Mongolian gerbil. Cancer Res. 1998;58(10):2067–2069. - PubMed
-
- Maruta F, Ota H, Genta RM, Sugiyama A, Tatematsu M, Katsuyama T, Kawasaki S. Role of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in the induction of intestinal metaplasia and gastric adenocarcinoma in Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2001;36(3):283–290. - PubMed
-
- Asaka M, Sugiyama T, Kato M, Satoh K, Kuwayama H, Fukuda Y, Fujioka T, Takemoto T, Kimura K, Shimoyama T, Shimizu K, Kobayashi S. A multicenter, double-blind study on triple therapy with lansoprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori in Japanese peptic ulcer patients. Helicobacter. 2001;6(3):254–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

