Elucidation of the Intestinal Absorption Mechanism of Loganin in the Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Model
- PMID: 30671130
- PMCID: PMC6323428
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8340563
Elucidation of the Intestinal Absorption Mechanism of Loganin in the Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Model
Abstract
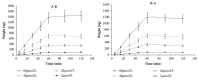
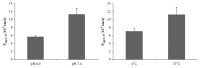
Loganin, iridoid glycosides, is the main bioactive ingredients in the plant Strychnos nux-vomica L. and demonstrates various pharmacological effects, though poor oral bioavailability in rats. In this study, the intestinal absorption mechanism of loganin was investigated using the human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayer model in both the apical-to-basolateral (A-B) and the basolateral-to-apical (B-A) direction; additionally, transport characteristics were systematically investigated at different concentrations, pHs, temperatures, and potential transporters. The absorption permeability (PappAB) of loganin, which ranged from 12.17 to 14.78 × 10-6cm/s, was high at four tested concentrations (5, 20, 40, and 80μM), while the major permeation mechanism of loganin was found to be passive diffusion with active efflux mediated by multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). In addition, it was found that loganin was not the substrate of efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) since the selective inhibitor (verapamil) of the efflux transporter exhibited little effects on the transport of loganin in the human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Meanwhile, transport from the apical to the basolateral side increased 2.09-fold after addition of a MRP inhibitor and 2.32-fold after addition of a BCRP inhibitor. In summary, our results clearly demonstrate, for the first time, a good permeability of loganin in the human intestinal Caco-2 cell model and elucidate, in detail, the intestinal absorption mechanism and the effects of transporters on iridoid glycosides compounds.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

