Flavonoid-Rich Ethanol Extract from the Leaves of Diospyros kaki Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation-Mediated Brain Aging in Mice
- PMID: 30671176
- PMCID: PMC6323539
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8938207
Flavonoid-Rich Ethanol Extract from the Leaves of Diospyros kaki Attenuates D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation-Mediated Brain Aging in Mice
Abstract
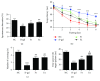
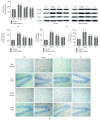
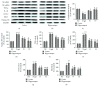
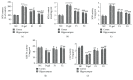
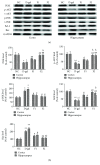
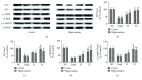
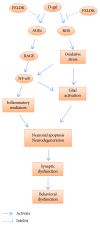
Aging is a major factor that contributes to neurological impairment and neuropathological changes, such as inflammation, oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and synaptic dysfunction. Flavonoids act as protective antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents against various age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we investigated the protective effect and mechanisms of the flavonoid-rich ethanol extract from the leaves of Diospyros kaki (FELDK) in the cortex and hippocampus of D-galactose- (gal-) aged mice. Our results showed that FELDK treatment restored memory impairment in mice as determined by the Y-maze and Morris water maze tests. FELDK decreased oxidative stress levels via inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) production and elevating antioxidative enzymes. FELDK also alleviated D-gal-induced neuroinflammation via suppressing the expression of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and receptor for AGEs (RAGE) and activating microgliosis and astrocytosis, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) nuclear translocation, and downstream inflammatory mediators. Moreover, FELDK inhibited the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and C-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) apoptotic signaling pathways and ameliorated the impairment of synapse-related proteins. Hence, these results indicate that FELDK exerts neuroprotective effects on D-gal-induced brain aging. Thus, FELDK may be a potential therapeutic strategy for preventing and treating age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anthocyanins Reversed D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Mediated Cognitive Impairment in Adult Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):255-271. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9604-5. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26738855
-
Flavonoid-rich ethanol extract from the leaves of Diospyros kaki attenuates cognitive deficits, amyloid-beta production, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Brain Res. 2018 Jan 1;1678:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29038004
-
Melatonin attenuates D-galactose-induced memory impairment, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via RAGE/NF-K B/JNK signaling pathway in aging mouse model.J Pineal Res. 2015 Jan;58(1):71-85. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12194. Epub 2014 Dec 9. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 25401971
-
A Review: Pharmacological Effect of Natural Compounds in Diospyros kaki Leaves from the Perspective of Oxidative Stress.Molecules. 2023 Dec 30;29(1):215. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010215. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Foods Containing Flavonoids on Age-Related Cognitive Decline.Curr Nutr Rep. 2018 Jun;7(2):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s13668-018-0227-0. Curr Nutr Rep. 2018. PMID: 29892789 Review.
Cited by
-
D-Galactose Induces Chronic Oxidative Stress and Alters Gut Microbiota in Weaned Piglets.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 8;12:634283. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.634283. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33897450 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic Acid B Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Injury by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via SIRT1-AMPK-PGC-1α Signaling Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022 Sep;22(9):842-857. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09760-8. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35809215
-
Effects of Grape Polyphenols on the Life Span and Neuroinflammatory Alterations Related to Neurodegenerative Parkinson Disease-Like Disturbances in Mice.Molecules. 2020 Nov 16;25(22):5339. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225339. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33207644 Free PMC article.
-
T1-11, an adenosine derivative, ameliorates aging-related behavioral physiology and senescence markers in aging mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 5;12(11):10556-10577. doi: 10.18632/aging.103279. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32501291 Free PMC article.
-
The protective role of miR-132 targeting HMGA2 through the PI3K/AKT pathway in mice with Alzheimer's disease.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):4632-4643. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150043 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

