Dissecting Aneurysm of the Internal Carotid Artery as a Complication of Facial Bone Trauma
- PMID: 30671188
- PMCID: PMC6330184
- DOI: 10.5001/omj.2019.12
Dissecting Aneurysm of the Internal Carotid Artery as a Complication of Facial Bone Trauma
Abstract
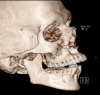
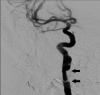
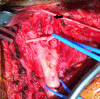
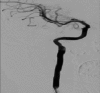
The involvement of the internal carotid artery in dissecting aneurysm is rarely reported in the literature and may occur as a complication of trauma, surgery, and other medical conditions. We report a case of a 22-year-old male who was involved in a motor vehicle accident with associated multiple orthopedic and maxillofacial fractures. During surgical management, the patient was incidentally diagnosed with a dissecting aneurysm involving the right internal carotid artery.
Keywords: Carotid Artery, Internal; Case Report; Dissecting Aneurysm; Facial Bones; Oman.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gradual Growth of Spontaneous Dissecting Aneurysm of the Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Turk Neurosurg. 2015;25(4):649-52. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9085-13.2. Turk Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26242345
-
Bilateral dissecting aneurysms of the intracranial internal carotid arteries in an 8-year-old boy.Neurology. 1975 Jun;25(6):573-9. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.6.573. Neurology. 1975. PMID: 1168877
-
[Massive epistaxis from intracranial extradural aneurysm of the internal carotid artery associated with head injury (author's transl)].No Shinkei Geka. 1976 Oct;4(10):953-61. No Shinkei Geka. 1976. PMID: 1033471 Japanese.
-
Ruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysm Concurrent with Spontaneous Cervical Internal Carotid Artery Dissection: A Report of Three Cases and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2017 Nov;107:1048.e1-1048.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.08.016. Epub 2017 Aug 9. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28803173 Review.
-
[Subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by a dissecting aneurysm of the internal carotid artery: case report and review of the literature].No Shinkei Geka. 2005 Aug;33(8):791-5. No Shinkei Geka. 2005. PMID: 16095209 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Giant Dissecting Aneurysm of the Internal Carotid Artery in a 35-Year-Old Patient: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Aug 20;16(8):e67353. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67353. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310566 Free PMC article.
-
Complications of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Mandibular Condyle Fractures in Oman.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024 Aug;24(3):338-344. doi: 10.18295/squmj.3.2024.020. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2024. PMID: 39234321 Free PMC article.
-
Re: Maxillary Artery Pseudoaneurysm as a Complication of Maxillofacial Injuries: Report of three cases and literature review.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2020 Nov;20(4):e401-e402. doi: 10.18295/squmj.2020.20.04.022. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2020. PMID: 33414951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
