Decreased protein binding of moxifloxacin in patients with sepsis?
- PMID: 30671325
- PMCID: PMC6301732
- DOI: 10.3205/id000029
Decreased protein binding of moxifloxacin in patients with sepsis?
Abstract
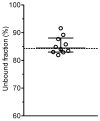
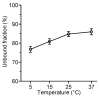
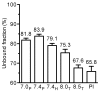
The mean (SD) unbound fraction of moxifloxacin in plasma from patients with severe sepsis or septic shock was determined by ultrafiltration to 85.5±3.0% (range 81.9 and 91.6%) indicating a decreased protein binding of moxifloxacin in this population compared with the value of 58-60% provided in the Summary of Product Characteristics. However, previous investigations neglected the influence of pH and temperature on the protein binding of moxifloxacin. Maintaining physiological conditions (pH 7.4, 37°C) - as in the present study - the unbound fraction of moxifloxacin in plasma from healthy volunteers was 84%. In contrast, the unbound fraction of moxifloxacin was 77% at 4°C and 66-68% in unbuffered plasma or at pH 8.5 in fair agreement with previously published data. PK/PD parameters e.g. fAUC/MIC or ratios between interstitial fluid and free plasma concentrations, which were obtained assuming a protein binding rate of moxifloxacin of 40% or more, should be revised.
Keywords: fluoroquinolone; septic shock; ultrafiltration; unbound fraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repeated determination of moxifloxacin concentrations in interstitial space fluid of muscle and subcutis in septic patients.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Sep 1;74(9):2681-2689. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz259. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31299075
-
Penetration of moxifloxacin into peripheral compartments in humans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Oct;43(10):2345-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.10.2345. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10508004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Experimental Variables on the Protein Binding of Tigecycline in Human Plasma as Determined by Ultrafiltration.J Pharm Sci. 2018 Feb;107(2):739-744. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 28927988
-
Protein binding in antiretroviral therapies.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2003 Sep;19(9):825-35. doi: 10.1089/088922203769232629. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2003. PMID: 14585213 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations when treating patients with sepsis and septic shock.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(14):1135-51. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241140-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12405864 Review.
Cited by
-
Host Biomarkers and Antibiotic Tissue Penetration in Sepsis: Insights from Moxifloxacin.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2025 Jul;50(4):289-294. doi: 10.1007/s13318-025-00945-4. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2025. PMID: 40268824 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers Predicting Tissue Pharmacokinetics of Antimicrobials in Sepsis: A Review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 May;61(5):593-617. doi: 10.1007/s40262-021-01102-1. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35218003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Model-Based Efficacy and Toxicity Comparisons of Moxifloxacin for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 29;9(3):ofab660. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofab660. eCollection 2022 Mar. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 35146045 Free PMC article.
-
Translational predictions of phase 2a first-in-patient efficacy studies for antituberculosis drugs.Eur Respir J. 2023 Aug 31;62(2):2300165. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00165-2023. Print 2023 Aug. Eur Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37321622 Free PMC article.
-
Free serum concentrations of antibiotics determined by ultrafiltration: extensive evaluation of experimental variables.Bioanalysis. 2024;16(14):747-756. doi: 10.1080/17576180.2024.2365526. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Bioanalysis. 2024. PMID: 39041640 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
