Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity: Recommendations from the Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition
- PMID: 30671370
- PMCID: PMC6333581
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.1.1
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity: Recommendations from the Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition
Abstract
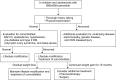
The Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition newly developed the first Korean Guideline on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Obesity in Children and Adolescents to deliver an evidence-based systematic approach to childhood obesity in South Korea. The following areas were systematically reviewed, especially on the basis of all available references published in South Korea and worldwide, and new guidelines were established in each area with the strength of recommendations based on the levels of evidence: 1) definition and diagnosis of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents; 2) principles of treatment of pediatric obesity; 3) behavioral interventions for children and adolescents with obesity, including diet, exercise, lifestyle, and mental health; 4) pharmacotherapy; and 5) bariatric surgery.
Keywords: Child; Diagnosis; Guideline; Obesity; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Guarino A, Albano F, Ashkenazi S, Gendrel D, Hoekstra JH, Shamir R, et al. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition; European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute gastroenteritis in children in Europe. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;46(Suppl 2):S81–S122. - PubMed