Frictional Keratosis, Contact Keratosis and Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis: Features of Reactive White Lesions of the Oral Mucosa
- PMID: 30671762
- PMCID: PMC6405791
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-018-0986-3
Frictional Keratosis, Contact Keratosis and Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis: Features of Reactive White Lesions of the Oral Mucosa
Abstract
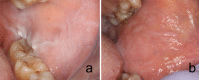
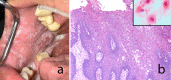
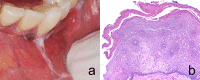
White lesions of the oral cavity are quite common and can have a variety of etiologies, both benign and malignant. Although the vast majority of publications focus on leukoplakia and other potentially malignant lesions, most oral lesions that appear white are benign. This review will focus exclusively on reactive white oral lesions. Included in the discussion are frictional keratoses, irritant contact stomatitis, and smokeless tobacco keratoses. Leukoedema and hereditary genodermatoses that may enter in the clinical differential diagnoses of frictional keratoses including white sponge nevus and hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis will be reviewed. Many products can result in contact stomatitis. Dentrifice-related stomatitis, contact reactions to amalgam and cinnamon can cause keratotic lesions. Each of these lesions have microscopic findings that can assist in patient management.
Keywords: Cinnamon; Frictional keratosis; Leukoedema; Leukoplakia; Smokeless tobacco keratosis; Stomatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The author declares they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Figures





References
-
- Sloan P, Gale N, Hunter K, et al. Malignant surface epithelial tumours: squamous cell carcinoma. In: el-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, Takata T, Slootweg PJ, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumours of the head and neck. 4. Lyon: IARC Press; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

