Adult neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus protects the hippocampus from neuronal injury following severe seizures
- PMID: 30672046
- PMCID: PMC6640126
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23062
Adult neurogenesis in the mouse dentate gyrus protects the hippocampus from neuronal injury following severe seizures
Abstract
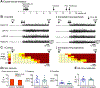
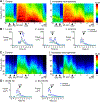
Previous studies suggest that reducing the numbers of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the mouse increases susceptibility to severe continuous seizures (status epilepticus; SE) evoked by systemic injection of the convulsant kainic acid (KA). However, it was not clear if the results would be the same for other ways to induce seizures, or if SE-induced damage would be affected. Therefore, we used pilocarpine, which induces seizures by a different mechanism than KA. Also, we quantified hippocampal damage after SE. In addition, we used both loss-of-function and gain-of-function methods in adult mice. We hypothesized that after loss-of-function, mice would be more susceptible to pilocarpine-induced SE and SE-associated hippocampal damage, and after gain-of-function, mice would be more protected from SE and hippocampal damage after SE. For loss-of-function, adult neurogenesis was suppressed by pharmacogenetic deletion of dividing radial glial precursors. For gain-of-function, adult neurogenesis was increased by conditional deletion of pro-apoptotic gene Bax in Nestin-expressing progenitors. Fluoro-Jade C (FJ-C) was used to quantify neuronal injury and video-electroencephalography (video-EEG) was used to quantify SE. Pilocarpine-induced SE was longer in mice with reduced adult neurogenesis, SE had more power and neuronal damage was greater. Conversely, mice with increased adult-born neurons had shorter SE, SE had less power, and there was less neuronal damage. The results suggest that adult-born neurons exert protective effects against SE and SE-induced neuronal injury.
Keywords: adult-born neurons; epilepsy; pilocarpine; progenitor; status epilepticus.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
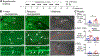

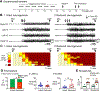
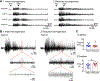
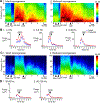


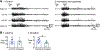

Similar articles
-
Increasing adult-born neurons protects mice from epilepsy.Elife. 2024 Oct 24;12:RP90893. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90893. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39446467 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of seizures, hippocampal injury and neurogenesis in three models of status epilepticus in galanin receptor type 1 (GalR1) knockout mice.Neuroscience. 2004;128(2):431-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.052. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 15350653 Free PMC article.
-
Increased gyrification and aberrant adult neurogenesis of the dentate gyrus in adult rats.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Dec;222(9):4219-4237. doi: 10.1007/s00429-017-1457-4. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 28656372 Free PMC article.
-
Seizure severity-dependent selective vulnerability of the granule cell layer and aberrant neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2017 Oct;27(10):1054-1068. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22752. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Hippocampus. 2017. PMID: 28608989
-
Immature dentate gyrus: an endophenotype of neuropsychiatric disorders.Neural Plast. 2013;2013:318596. doi: 10.1155/2013/318596. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 23840971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increasing adult-born neurons protects mice from epilepsy.Elife. 2024 Oct 24;12:RP90893. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90893. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39446467 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Neurogenesis in the Development of Epilepsy.Epilepsy Curr. 2019 Sep;19(5):316-320. doi: 10.1177/1535759719868186. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Epilepsy Curr. 2019. PMID: 31409149 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 impairs cognition in systemic lupus erythematosus by promoting microglial synaptic pruning via the β-catenin signaling pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Oct 13;18(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02279-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34645459 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Grafting after Status Epilepticus Alleviates Chronic Epilepsy and Abnormal Plasticity, and Maintains Better Memory and Mood Function.Aging Dis. 2020 Dec 1;11(6):1374-1394. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.1020. eCollection 2020 Dec. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 33269095 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Epilepsies and Associated Comorbidities: Implications for Use and Development of Pharmacotherapies.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Oct;72(4):767-800. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.017392. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32817274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman J, Das GD (1965). Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol, 124(3), 319–335. - PubMed
-
- Altman J (2011). The discovery of adult mammalian neurogenesis In Seki T, Sawamoto K, Parent JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (Eds.), Neurogenesis in the Adult Brain I: Neurobiology (Vol. I, pp. 3–46): Springer.
-
- Amaral DG (1978). A Golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol, 182, 851–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

