JS-K induces reactive oxygen species-dependent anti-cancer effects by targeting mitochondria respiratory chain complexes in gastric cancer
- PMID: 30672108
- PMCID: PMC6433691
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14122
JS-K induces reactive oxygen species-dependent anti-cancer effects by targeting mitochondria respiratory chain complexes in gastric cancer
Abstract
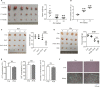
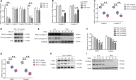
As a nitric oxide (NO) donor prodrug, JS-K inhibits cancer cell proliferation, induces the differentiation of human leukaemia cells, and triggers apoptotic cell death in various cancer models. However, the anti-cancer effect of JS-K in gastric cancer has not been reported. In this study, we found that JS-K inhibited the proliferation of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo and triggered mitochondrial apoptosis. Moreover, JS-K induced a significant accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the clearance of ROS by antioxidant reagents reversed JS-K-induced toxicity in gastric cancer cells and subcutaneous xenografts. Although JS-K triggered significant NO release, NO scavenging had no effect on JS-K-induced toxicity in vivo and in vitro. Therefore, ROS, but not NO, mediated the anti-cancer effects of JS-K in gastric cancer. We also explored the potential mechanism of JS-K-induced ROS accumulation and found that JS-K significantly down-regulated the core proteins of mitochondria respiratory chain (MRC) complex I and IV, resulting in the reduction of MRC complex I and IV activity and the subsequent ROS production. Moreover, JS-K inhibited the expression of antioxidant enzymes, including copper-zinc-containing superoxide dismutase (SOD1) and catalase, which contributed to the decrease of antioxidant enzymes activity and the subsequent inhibition of ROS clearance. Therefore, JS-K may target MRC complex I and IV and antioxidant enzymes to exert ROS-dependent anti-cancer function, leading to the potential usage of JS-K in the prevention and treatment of gastric cancer.
Keywords: JS-K; apoptosis; gastric cancer; mitochondria respire chain complex; nitric oxide; reactive oxygen species.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures





References
-
- Maciag AE, Saavedra JE, Chakrapani H. The nitric oxide prodrug JS‐K and its structural analogues as cancer therapeutic agents. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009;9:798‐803. - PubMed
-
- Shami PJ, Saavedra JE, Bonifant CL, et al. Antitumor activity of JS‐K [O2‐(2,4‐dinitrophenyl) 1‐[(4‐ethoxycarbonyl)piperazin‐1‐yl]diazen‐1‐ium‐1,2‐diolate] and related O2‐aryl diazeniumdiolates in vitro and in vivo. J Med Chem. 2006;49:4356‐4366. - PubMed
-
- Shami PJ, Saavedra JE, Wang LY, et al. JS‐K, a glutathione/glutathione S‐transferase‐activated nitric oxide donor of the diazeniumdiolate class with potent antineoplastic activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:409‐417. - PubMed
-
- Udupi V, Yu M, Malaviya S, et al. JS‐K, a nitric oxide prodrug, induces cytochrome c release and caspase activation in HL‐60 myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2006;30:1279‐1283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

