GATA5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells malignant behaviours by blocking expression of reprogramming genes
- PMID: 30672133
- PMCID: PMC6433710
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14144
GATA5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells malignant behaviours by blocking expression of reprogramming genes
Abstract
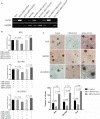
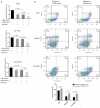
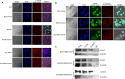
Evidence indicated that GATA5 may suppress hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell malignant transformation, but the mechanism of how GATA5 affects cancer cell reprogramming to inhibit HCC malignant behaviour is still unclear. In this study, we report that the expression of β-catenin and reprogramming genes p-Oct4, Nanog, Klf4, c-myc and EpCAM was significantly higher in HCC tissues compared to normal liver tissues. In contrast, the expression of GATA5 was significantly lower in HCC tissues compared to normal liver tissues. Transfection of CDH-GATA5 vectors into HCC cells (HLE, Bel 7402 and PLC/PRF/5 cells) increased the GATA5 expression and decreased the expression of β-catenin and reprogramming genes p-Oct4, Nanog, Klf4, c-myc and EpCAM. Increased GATA5 expression by transfection with its expression vectors was also able to inhibit the cell growth, colony formation and capability of migration, invasion, while promoting apoptosis in HCC cells. Results revealed that GATA5 co-localization with β-catenin in the cytoplasm, preventing β-catenin from entering the nucleus. Treatment with the specific Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor salinomycin was able to reduce the expression of β-catenin and reprogramming genes. Salinomycin exerted a similar influence as GATA5, and siRNA-GATA5 restored β-catenin and reprogramming gene expression. This study demonstrates that an increase in the expression of GATA5 inhibits the expression of β-catenin and reprogramming genes and suppresses tumour growth, colony formation, metastasis and invasion, while promoting apoptosis in HCC cells. The mechanism of GATA5 inhibiting the malignant behaviours of HCC cells may involve in the disruption of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and the reduction of reprogramming gene expression.
Keywords: GATA5 expression; HCC; Wnt/β-catenin; reprogramming genes; stemness marker.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
WM130 preferentially inhibits hepatic cancer stem-like cells by suppressing AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79544-79556. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12822. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783993 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop involving the LINC00346/β-catenin/MYC axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Feb;43(1):137-153. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00478-4. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31691159
-
Jiedu Recipe, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, inhibits cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway under hypoxia.J Integr Med. 2023 Sep;21(5):474-486. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2023.06.008. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37453868
-
Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 14;22(2):823-32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.823. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26811628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular reprogramming and hepatocellular carcinoma development.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 21;19(47):8850-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8850. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of GATA5 Stimulates Paclitaxel to Inhibit Malignant Behaviors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Cell J. 2020 Jul;22(Suppl 1):89-100. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2020.6894. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Cell J. 2020. PMID: 32779438 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile and prognostic values of GATA family members in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 23;15(6):2170-2188. doi: 10.18632/aging.204607. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36961416 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors That Govern Development and Disease: An Achilles Heel in Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2019 Oct 12;10(10):794. doi: 10.3390/genes10100794. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeobox Genes and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 3;11(5):621. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050621. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31058850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vincosamide Has a Function for Inhibiting Malignant Behaviors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.World J Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):272-288. doi: 10.14740/wjon1514. Epub 2022 Oct 22. World J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36406198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Ge S, Huang D. Systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Discov Ther. 2015;9:352‐362. - PubMed
-
- Feng X, Xu R, Du X, et al. Combination therapy with sorafenib and radiofrequency ablation for BCLC stage 0–B1 hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1891‐1899. - PubMed
-
- Thorgeirsson SS, Grisham JW. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31:339‐346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

