Accelerated Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography with Sparse Undersampling and Iterative Reconstruction for the Evaluation of Intracranial Arteries
- PMID: 30672166
- PMCID: PMC6342758
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2017.0634
Accelerated Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography with Sparse Undersampling and Iterative Reconstruction for the Evaluation of Intracranial Arteries
Abstract
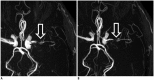
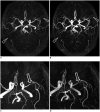
Objective: To compare the image quality of three-dimensional time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) with sparse undersampling and iterative reconstruction (sparse TOF) with that of conventional TOF MRA.
Materials and methods: This study included 56 patients who had undergone sparse TOF MRA for intracranial artery evaluation on a 3T MR scanner. Conventional TOF MRA scans were also acquired from 29 patients with matched acquisition times and another 27 patients with matched scanning parameters. The image quality was scored using a five-point scale based on the delineation of arterial vessel segments, artifacts, overall vessel visualization, and overall image quality by two radiologists independently, and the data were analyzed using the non-parametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Contrast ratios (CRs) of vessels were compared using the paired t test. Interobserver agreement was calculated using the kappa test.
Results: Compared with conventional TOF at the same spatial resolution, sparse TOF with an acceleration factor of 3.5 could reduce acquisition time by 40% and showed comparable image quality. In addition, when compared with conventional TOF with the same acquisition time, sparse TOF with an acceleration factor of 5 could also achieve higher spatial resolution, better delineation of vessel segments, fewer artifacts, higher image quality, and a higher CR (p < 0.05). Good-to-excellent interobserver agreement (κ: 0.65-1.00) was obtained between the two radiologists.
Conclusion: Compared with conventional TOF, sparse TOF can achieve equivalent image quality in a reduced duration. Furthermore, using the same acquisition time, sparse TOF could improve the delineation of vessels and decrease image artifacts.
Keywords: Intracranial vessels; Iterative reconstruction; Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA); Sparse; Time-of-Flight (TOF).
Copyright © 2019 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography With Sparse Undersampling and Iterative Reconstruction: Comparison With Conventional Parallel Imaging for Accelerated Imaging.Invest Radiol. 2016 Jun;51(6):372-8. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000221. Invest Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26561046
-
3 T contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for evaluation of the intracranial arteries: comparison with time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography and multislice computed tomography angiography.Invest Radiol. 2006 Nov;41(11):799-805. doi: 10.1097/01.rli.0000242835.00032.f5. Invest Radiol. 2006. PMID: 17035870 Clinical Trial.
-
Highly accelerated time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography using spiral imaging improves conspicuity of intracranial arterial branches while reducing scan time.Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):855-865. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06442-y. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31664504
-
Clinical evaluation of time-of-flight MR angiography with sparse undersampling and iterative reconstruction for cerebral aneurysms.NMR Biomed. 2017 Nov;30(11). doi: 10.1002/nbm.3774. Epub 2017 Aug 10. NMR Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28796397
-
Artifacts associated with MR neuroangiography.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Sep-Oct;13(5):1411-22. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992. PMID: 1414835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Anesthetic Procedures for Ferret (Mustela putorius furo) Preclinical Brain MRI: A Call for Standardization.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 1;64(1):16-28. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-24-086. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of 3.0T magnetic resonance angiography for the detection of arteriovenous fistula dysfunction in hemodialysis patients requiring interventional therapy: a prospective study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Apr 3;14(4):2788-2799. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1505. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38617180 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Analysis of Carotid Artery Through Bilateral 3D Modeling via MRI and DICOM Processing.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 1;12(2):142. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12020142. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001662 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical feasibility of CS-VIBE accelerates MRI techniques in diagnosing intracranial metastasis.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 20;13(1):10012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37148-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37340077 Free PMC article.
-
[Application of 3.0T Time-of-flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography with Sparse Undersampling and Iterative Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Jan;52(1):92-97. doi: 10.12182/20210160602. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 33474896 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Keller PJ, Drayer BP, Fram EK, Williams KD, Dumoulin CL, Souza SP. MR angiography with two-dimensional acquisition and three-dimensional display. Work in progress. Radiology. 1989;173:527–532. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki M, Akahane M. Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: established techniques. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Wheaton AJ, Miyazaki M. Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: physical principles. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36:286–304. - PubMed
-
- Laub GA. Time-of-flight method of MR angiography. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1995;3:391–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

