Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults
- PMID: 30673120
- PMCID: PMC6353204
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007076.pub3
Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults
Abstract
Background: This review updates part of an earlier Cochrane Review titled "Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults", and considers only neuropathic pain (pain from damage to nervous tissue). Antiepileptic drugs have long been used in pain management. Pregabalin is an antiepileptic drug used in management of chronic pain conditions.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of pregabalin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and Embase for randomised controlled trials from January 2009 to April 2018, online clinical trials registries, and reference lists.
Selection criteria: We included randomised, double-blind trials of two weeks' duration or longer, comparing pregabalin (any route of administration) with placebo or another active treatment for neuropathic pain, with participant-reported pain assessment.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality and biases. Primary outcomes were: at least 30% pain intensity reduction over baseline; much or very much improved on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) Scale (moderate benefit); at least 50% pain intensity reduction; or very much improved on PGIC (substantial benefit). We calculated risk ratio (RR) and number needed to treat for an additional beneficial (NNTB) or harmful outcome (NNTH). We assessed the quality of the evidence using GRADE.
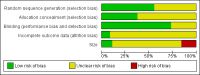
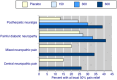
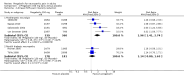
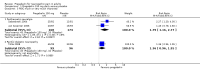
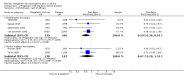
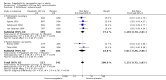
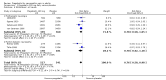
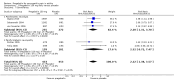
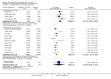
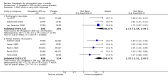
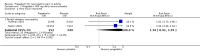
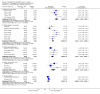
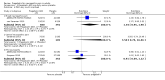
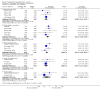
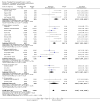
Main results: We included 45 studies lasting 2 to 16 weeks, with 11,906 participants - 68% from 31 new studies. Oral pregabalin doses of 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg daily were compared with placebo. Postherpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuropathy, and mixed neuropathic pain predominated (85% of participants). High risk of bias was due mainly to small study size (nine studies), but many studies had unclear risk of bias, mainly due to incomplete outcome data, size, and allocation concealment.Postherpetic neuralgia: More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 300 mg than with placebo (50% vs 25%; RR 2.1 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.6 to 2.6); NNTB 3.9 (3.0 to 5.6); 3 studies, 589 participants, moderate-quality evidence), and more had at least 50% pain intensity reduction (32% vs 13%; RR 2.5 (95% CI 1.9 to 3.4); NNTB 5.3 (3.9 to 8.1); 4 studies, 713 participants, moderate-quality evidence). More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 600 mg than with placebo (62% vs 24%; RR 2.5 (95% CI 2.0 to 3.2); NNTB 2.7 (2.2 to 3.7); 3 studies, 537 participants, moderate-quality evidence), and more had at least 50% pain intensity reduction (41% vs 15%; RR 2.7 (95% CI 2.0 to 3.5); NNTB 3.9 (3.1 to 5.5); 4 studies, 732 participants, moderate-quality evidence). Somnolence and dizziness were more common with pregabalin than with placebo (moderate-quality evidence): somnolence 300 mg 16% versus 5.5%, 600 mg 25% versus 5.8%; dizziness 300 mg 29% versus 8.1%, 600 mg 35% versus 8.8%.Painful diabetic neuropathy: More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 300 mg than with placebo (47% vs 42%; RR 1.1 (95% CI 1.01 to 1.2); NNTB 22 (12 to 200); 8 studies, 2320 participants, moderate-quality evidence), more had at least 50% pain intensity reduction (31% vs 24%; RR 1.3 (95% CI 1.2 to 1.5); NNTB 22 (12 to 200); 11 studies, 2931 participants, moderate-quality evidence), and more had PGIC much or very much improved (51% vs 30%; RR 1.8 (95% CI 1.5 to 2.0); NNTB 4.9 (3.8 to 6.9); 5 studies, 1050 participants, moderate-quality evidence). More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 600 mg than with placebo (63% vs 52%; RR 1.2 (95% CI 1.04 to 1.4); NNTB 9.6 (5.5 to 41); 2 studies, 611 participants, low-quality evidence), and more had at least 50% pain intensity reduction (41% vs 28%; RR 1.4 (95% CI 1.2 to 1.7); NNTB 7.8 (5.4 to 14); 5 studies, 1015 participants, low-quality evidence). Somnolence and dizziness were more common with pregabalin than with placebo (moderate-quality evidence): somnolence 300 mg 11% versus 3.1%, 600 mg 15% versus 4.5%; dizziness 300 mg 13% versus 3.8%, 600 mg 22% versus 4.4%.Mixed or unclassified post-traumatic neuropathic pain: More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 600 mg than with placebo (48% vs 36%; RR 1.2 (1.1 to 1.4); NNTB 8.2 (5.7 to 15); 4 studies, 1367 participants, low-quality evidence), and more had at least 50% pain intensity reduction (34% vs 20%; RR 1.5 (1.2 to 1.9); NNTB 7.2 (5.4 to 11); 4 studies, 1367 participants, moderate-quality evidence). Somnolence (12% vs 3.9%) and dizziness (23% vs 6.2%) were more common with pregabalin.Central neuropathic pain: More participants had at least 30% pain intensity reduction with pregabalin 600 mg than with placebo (44% vs 28%; RR 1.6 (1.3 to 2.0); NNTB 5.9 (4.1 to 11); 3 studies, 562 participants, low-quality evidence) and at least 50% pain intensity reduction (26% vs 15%; RR 1.7 (1.2 to 2.3); NNTB 9.8 (6.0 to 28); 3 studies, 562 participants, low-quality evidence). Somnolence (32% vs 11%) and dizziness (23% vs 8.6%) were more common with pregabalin.Other neuropathic pain conditions: Studies show no evidence of benefit for 600 mg pregabalin in HIV neuropathy (2 studies, 674 participants, moderate-quality evidence) and limited evidence of benefit in neuropathic back pain or sciatica, neuropathic cancer pain, or polyneuropathy.Serious adverse events, all conditions: Serious adverse events were no more common with placebo than with pregabalin 300 mg (3.1% vs 2.6%; RR 1.2 (95% CI 0.8 to 1.7); 17 studies, 4112 participants, high-quality evidence) or pregabalin 600 mg (3.4% vs 3.4%; RR 1.1 (95% CI 0.8 to 1.5); 16 studies, 3995 participants, high-quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: Evidence shows efficacy of pregabalin in postherpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuralgia, and mixed or unclassified post-traumatic neuropathic pain, and absence of efficacy in HIV neuropathy; evidence of efficacy in central neuropathic pain is inadequate. Some people will derive substantial benefit with pregabalin; more will have moderate benefit, but many will have no benefit or will discontinue treatment. There were no substantial changes since the 2009 review.
Conflict of interest statement
SD: none known.
RFB: none known. RFB is a retired specialist pain physician who has managed patients with neuropathic pain.
SS: none known. Sebastian Straube is a specialist occupational medicine physician.
PW: none known.
DA has received honoraria from Mundipharma and Grunenthal UK for presentations and expert opinion since 2015. DA is a pain physician who treats patients with neuropathic pain. He also works pro bono for various veterans charities in the UK.
RAM has received honoraria from Omega Pharma/Perrigo Pharma (2016, 2017), Futura Pharma (2015, 2016), RB (2015, 2017, 2018), and the Advertising Standards Authority (2016) for providing advice on trial and data analysis methods. He has received honoraria for lectures from Novartis (2016) and RB (2018).
Figures





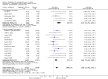
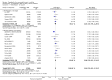
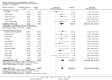
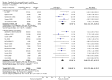


Update of
-
Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8;(3):CD007076. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007076.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 23;1:CD007076. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007076.pub3. PMID: 19588419 Free PMC article. Updated.
Comment in
-
Patient-reported improvement in pain with pregabalin for painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia is promising but needs further investigation.Evid Based Nurs. 2020 Jan;23(1):17. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2019-103091. Epub 2019 May 15. Evid Based Nurs. 2020. PMID: 31092541 No abstract available.
-
Should Pregabalin Be Used in the Management of Chronic Neuropathic Pain in Adults? A Cochrane Review Summary With Commentary.PM R. 2019 Dec;11(12):1360-1363. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.12283. PM R. 2019. PMID: 31729182 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
1008‐030 {unpublished data only}
-
- Pfizer (Sponsor). None known. WC500046600_EMEA found at http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_‐_Scientific_D... 2004 (accessed 27 April 2018). [Pfizer: 1008‐030]
1008‐040 {unpublished data only}
-
- Pfizer (Sponsor). None known. WC500046600_EMEA found at http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_‐_Scientific_D... 2004 (accessed 27 April 2018). [Pfizer: 1008‐040]
A0081030 [NCT00156078] {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hoffman DL, Sadosky A, Dukes EM, Alvir J. How do changes in pain severity levels correspond to changes in health status and function in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy?. Pain 2010;149(2):194‐201. [CTG: NCT00156078; DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.09.017; Pfizer: A0081030] - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCT00156078. A 14‐week, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled, multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of pregabalin (150 mg‐600 mg/day) using a flexible optimal dose schedule in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00156078 (first received 12 September 2005). [ClinicaTrials.gov: NCT00156078 ]
A0081071 [NCT00143156] {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multi‐center trial of pregabalin versus placebo in the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. PhRMA Clinical Study Synopsis 19 December 2007. [CTG: NCT00143156; Pfizer: A0081071]
A0081244 [NCT01049217] {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter trial of pregabalin versus placebo in the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with HIV neuropathy. 2014. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 12 June 2017). [CTG: NCT01049217; Pfizer: A0081244]
A0081279 [NCT01701362] {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized double blind placebo controlled parallel group study of the efficacy and safety of pregabalin (BID) in subjects with post‐traumatic peripheral neuropathic pain. 2016. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 12 June 2017). [NCT01701362; Pfizer: A0081279]
A9011015 [NCT01117766] {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, 2‐way crossover methodology study designed to assess the reproducibility and sensitivity of quantitative sensory testing (QST) in patients with neuropathic pain treated with pregabalin vs placebo. 2010. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 12 June 2017). [CTG: NCT01117766; Pfizer: A9011015]
Arezzo 2008 {published data only}
Bansal 2009 {published data only}
Baron 2010 {published data only}
Cardenas 2013 {published data only}
Dou 2017 {published data only}
Dworkin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dworkin RH, Corbin AE, Young JP Jr, Sharma U, LaMoreaux L, Bockbrader H, et al. Pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 2003;60:1274‐83. [DOI: 10.%E2%80%8B1212/%E2%80%8B01.%E2%80%8BWNL.%E2%80%8B0000055433.%E2%80%8B55136.%E2%80%8B55] - DOI - PubMed
Freynhagen 2005 {published data only}
Gilron 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gilron I, Wajsbrot D, Therrien F, Lemay J. Pregabalin for peripheral neuropathic pain: a multicenter, enriched enrollment randomized withdrawal placebo‐controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2011;27(3):185‐93. [CTG: NCT00219544; Pfizer: A0081064] - PubMed
González‐Duarte 2016 {published data only}
Guan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Guan Y, Ding X, Cheng Y, Fan D, Tan L, Wang Y, et al. Efficacy of pregabalin for peripheral neuropathic pain: results of an 8‐week, flexible‐dose, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study conducted in China. Clinical Therapeutics 2011;33(2):159‐66. [CTG: NCT00301223; DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.02.007; Pfizer: A0081081] - DOI - PubMed
Hewitt 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hewitt DJ, Ho TW, Galer B, Backonja M, Markovitz P, Gammaitoni A, et al. Impact of responder definition on the enriched enrollment randomized withdrawal trial design for establishing proof of concept in neuropathic pain. Pain 2011;152(3):514‐21. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.10.050; NCT00570310] - DOI - PubMed
Holbech 2015 {published data only}
Huffman 2015 {published data only}
-
- Huffman C, Stacey BR, Tuchman M, Burbridge C, Li C, Parsons B, et al. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in the treatment of patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy and pain on walking. Clinical Journal of Pain 2015;31(11):946‐58. [CTG: NCT01474772; DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000198; EudraCT : 2011‐003266‐32; Pfizer: A0081269] - DOI - PubMed
Huffman 2017 {published data only}
-
- Huffman CL, Goldenberg JN, Weintraub J, Sanin L, Driscoll J, Yang R, et al. Efficacy and safety of once‐daily controlled‐release pregabalin for the treatment of patients with postherpetic neuralgia: a double‐blind, randomized withdrawal, placebo‐controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2017;33(7):569‐78. [CinicalTrials.gov: NCT01270828; DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000445; EudraCT: 2009‐016766‐86; Pfizer: A0081224] - DOI - PubMed
Kim 2011 {published data only}
Lesser 2004 {published data only}
Liu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Liu Q, Chen H, Xi L, Hong Z, He L, Fu Y, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pregabalin for postherpetic neuralgia in a population of Chinese patients. Pain Practice 2017;17(1):62‐9. [CTG: NCT01455428; DOI: 10.1111/papr.12413; Pfizer: A0081276] - DOI - PubMed
Mishra 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mishra S, Bhatnagar S, Goyal GN, Rana SP, Upadhya SP. A comparative efficacy of amitriptyline, gabapentin, and pregabalin in neuropathic cancer pain: a prospective randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care 2012;29(3):177‐82. [DOI: 10.1177/1049909111412539] - DOI - PubMed
Moon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moon DE, Lee DI, Lee SC, Song SO, Yoon DM, Yoon MH, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of pregabalin using a flexible, optimized dose schedule in Korean patients with peripheral neuropathic pain: a 10‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter study. Clinical Therapeutics 2010;32(14):2370‐85. [CTG: NCT00141219; DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.01.014; Pfizer: A0081037] - DOI - PubMed
Mu 2018 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mu Y, Liu X, Li Q, Chen K, Liu Y, Lv X, et al. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a population of Chinese patients: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Diabetes 2018;10(3):256‐65. [CTG: NCT01332149; DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.12585; Pfizer: A0081265] - DOI - PubMed
NCT00785577 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00785577. A phase 2 study of the effects of LY545694, an iGluR5 antagonist, in the treatment of subjects with painful diabetic neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00785577 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 5 November 2008). [CTG: NCT00785577; Eli Lilly: H8C‐MC‐LQBF]
Ogawa 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ogawa S, Suzuki M, Arakawa A, Araki S, Yoshiyama T. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of pregabalin in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Japan Society of Pain Clinicians 2010;17(2):141‐52. [CTG: NCT00394901; Pfizer: A0081120]
Raskin 2014 {published data only}
-
- Raskin P, Huffman C, Toth C, Asmus MJ, Messig M, Sanchez RJ, et al. Pregabalin in patients with inadequately treated painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized withdrawal trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2014;30(5):379‐90. [CTG: NCT01057693; DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e31829ea1a1; Pfizer: A0081242] - DOI - PubMed
Raskin 2016 {published data only}
-
- Raskin P, Huffman C, Yurkewicz L, Pauer L, Scavone JM, Yang R, et al. Pregabalin in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy using an NSAID for other pain conditions: a double‐blind crossover study. Clinical Journal of Pain 2016;32(3):203‐10. [CTG: NCT01455415; DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000254; Pfizer: A0081268] - DOI - PubMed
Rauck 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rauck R, Makumi CW, Schwartz S, Graff O, Meno‐Tetang G, Bell CF, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Practice 2013;13(6):485‐96. [ClinicslTrials.gov: NCT00643760; DOI: 10.1111/papr.12014; PXN110448] - DOI - PubMed
Richter 2005 {published data only}
Rosenstock 2004 {published data only}
Sabatowski 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sabatowski R, Galvez R, Cherry DA, Jacquot F, Vincent E, 1008‐ 045 Study Group, et al. Pregabalin reduces pain and improves sleep and mood disturbances in patients with post‐herpetic neuralgia: results of a randomised, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Pain 2004;109:26‐35. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.01.001; 1008‐045] - DOI - PubMed
Satoh 2011 {published data only}
-
- Satoh J, Yagihashi S, Baba M, Suzuki M, Arakawa A, Yoshiyama T, et al. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin for treating neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a 14 week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Diabetic Medicine 2011;28(1):109‐16. [CTG: NCT00553475; DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03152.x; Pfizer: A0081163] - DOI - PubMed
Siddall 2006 {published data only}
Simpson 2010 {published data only}
Smith 2014 {published data only}
-
- Smith T, DiBernardo A, Shi Y, Todd MJ, Brashear HR, Ford LM. Efficacy and safety of carisbamate in patients with diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia: results from 3 randomized, double‐blind placebo‐controlled trials. Pain Practice 2014;14(4):332‐42. [CTG: NCT00870454; DOI: 10.1111/papr.12080; EudraCT: 2008‐008753‐33; CR015973] - DOI - PubMed
Stacey 2008 {published data only}
-
- Stacey BR, Barrett JA, Whalen E, Phillips KF, Rowbotham MC. Pregabalin for postherpetic neuralgia: placebo‐controlled trial of fixed and flexible dosing regimens on allodynia and time to onset of pain relief. Journal of Pain 2008;9(11):1006‐17. [CTG: NCT00159666; DOI: 10.1016/j,pain.2008.05.014; Pfizer: A0081004] - DOI - PubMed
Tölle 2008 {published data only}
van Seventer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Seventer R, Feister HA, Young JP Jr, Stoker M, Versavel M, Rigaudy L. Efficacy and tolerability of twice‐daily pregabalin for treating pain and related sleep interference in postherpetic neuralgia: a 13‐week, randomized trial. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(2):375‐84. [DOI: 10.1185/030079906X80404] - DOI - PubMed
van Seventer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Seventer R, Bach FW, Toth CC, Serpell M, Temple J, Murphy TK, et al. Pregabalin in the treatment of post‐traumatic peripheral neuropathic pain: a randomized double‐blind trial. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17(8):1082‐9. [CTG: NCT00292188; DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02979.x; Pfizer: A0081064] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seventer R, Serpell M, Bach FW, Morlion B, Zlateva G, Bushmakin AG, et al. Relationships between changes in pain severity and other patient‐reported outcomes: an analysis in patients with posttraumatic peripheral neuropathic pain. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2011;9:17. [DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-9-17] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Vinik 2014 {published data only}
-
- Vinik A, Rosenstock J, Sharma U, Feins K, Hsu C, Merante D, et al. Efficacy and safety of mirogabalin (DS‐5565) for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active comparator‐controlled, adaptive proof‐of‐concept phase 2 study. Diabetes Care 2014;37(12):3253‐61. [CTG: NCT01496365; DOI: 10.2337/dc14-1044] - DOI - PubMed
Ziegler 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ziegler D, Duan WR, An G, Thomas JW, Nothaft W. A randomized double‐blind, placebo‐, and active‐controlled study of T‐type calcium channel blocker ABT‐639 in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2015;156(10):2013‐20. [CTG: NCT01345045; DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000263; EudraCT: 2010‐024359‐99; M11‐891] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
A0081128 {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized placebo‐controlled trial of the efficacy and tolerability of flexibly dosed pregabalin in the treatment of cancer‐induced bone pain. 12 December 2014. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 2 May 2018). [NCT00381095; Pfizer: A0081128]
A0081187 [NCT00654940] {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A methodology study to assess the ability of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, two period crossover study to detect the effect of pregabalin in post‐traumatic neuropathic pain patients. 2014. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 12 June 2017). [Pfizer: A0081187]
A0081296 {unpublished data only}
-
- Anon. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group study of the efficacy and safety of concomitant administration of celecoxib and pregabalin compared with celecoxib monotherapy, in patients with chronic low back pain having a neuropathic component. 4 July 2016. pfizer.com/science/research_clinical_trials/trial_results (accessed 12 June 2017). [CTG: NCT01838044; Pfizer: A0081296]
Boyle 2012 {published data only}
-
- Boyle J, Eriksson ME, Gribble L, Gouni R, Johnsen S, Coppini DV, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled comparison of amitriptyline, duloxetine, and pregabalin in patients with chronic diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: impact on pain, polysomnographic sleep, daytime functioning, and quality of life. Diabetes Care 2012;35(12):2451‐8. [CTG: NCT00370656; DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0656; CRC 235] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
CTRI/2013/05/003646 {published data only}
-
- Shende SD (Principal Investigator). A prospective, controlled, randomized, double blind, comparative, parallel, 2‐arm study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Epalrestat (150 mg) compared to Pregabalin (600 mg) in patients suffering from painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=6445 (accessed 13 February 2018). [ICTRP: CTRI/2013/05/003646; EP/PDN/12/2012]
Mathieson 2017 {published data only}
NCT00787462 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00787462. Evaluation of pregabalin in idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00787462 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 7 November 2008). [CTG: NCT00787462]
NCT00908375 {published data only}
-
- NCT00908375. Efficacy of pregabalin in patients with radicular pain. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00908375 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 25 May 2009). [CTG: NCT00908375]
NCT01058642 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01058642. A phase 2A, randomized, blinded, placebo‐ and active‐controlled, 2‐period crossover study to assess the analgesic efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ADL5747 in subjects with postherpetic neuralgia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01058642 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 29 January 2010). [CTG: NCT01058642; 40CL234]
NCT01089556 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01089556. Use of duloxetine or pregabalin in monotherapy versus combination therapy of both drugs in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy: "The COMBO ‐ DN (COmbination vs Monotherapy of pregaBalin and dulOxetine in Diabetic Neuropathy) Study". clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01089556 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 18 March 2010). [CTG: NCT01089556; Eli Lilly: F1J‐EW‐HMGQ; 13084]
NCT01180608 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01180608. Functional imaging of the therapeutic effect of pregabalin in treatment for neuropathic pain in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy using proton MR spectroscopy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01180608 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 12 August 2010). [CTG: NCT01180608]
NCT01928381 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01928381. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled crossover study to evaluate the preliminary efficacy of AZD5213 in combination with pregabalin in subjects with painful diabetic neuropathy and good pain reporting ability. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01928381 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 23 August 2013). [CTG: NCT01928381; D3031C00001]
NCT02215252 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02215252. A randomized double blind placebo and active controlled parallel group phase 2 study to evaluate PF‐05089771 as a monotherapy and as an add‐on to pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02215252 (accessed 2 May 2018) (first posted 13 August 2014). [B3291026 ; DPN NAV1.7; NCT02215252]
NCT02372578 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02372578. A phase 2a randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, placebo and active controlled study to assess analgesic efficacy and safety of ASP3662 in subjects with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02372578 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 26 February 2015). [CTG: NCT02372578; 3662‐CL‐0049]
Razazian 2014 {published data only}
-
- Razazian N1, Baziyar M, Moradian N, Afshari D, Bostani A, Mahmoodi M. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of pregabalin, venlafaxine, and carbamazepine in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A randomized, double‐blind trial. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2014;19(3):192‐8. [IRCT201302188323N6; PUBMED: PMC4727652] - PMC - PubMed
Romano 2009 {published data only}
Vranken 2008 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
IRCT201602112027N5 {published data only}
-
- Anon. Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of pregabalin and duloxetine in peripheral neuropathy induced by taxanes containing chemotherapy regimens in women with breast cancer, a randomized clinical trial. 2016. who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=IRCT201602112027N5 (accessed 13 February 2018). [IRCT201602112027N5]
NCT00838799 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00838799. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled study of the safety and efficacy of RGH‐896 in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00838799 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 6 February 2009). [CTG: NCT00838799; RG8‐MD‐02]
NCT01314222 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01314222. A randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled, cross‐over study of the efficacy and safety of BMS‐954561 in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (DPNP). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/ NCT01314222 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 14 March 2011). [CTG: NCT01314222; EudraCT: 2010‐023042‐70; CN169‐001]
NCT01479556 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01479556. Assessment of pregabalin efficacy for the treatment and prevention of at‐level non‐evoked and evoked spinal cord injury neuropathic pain. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01479556 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 24 November 2011). [CTG: NCT01479556; EudraCT: 2011‐000915‐14; HNP‐02‐2011]
NCT01504412 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01504412. An Asian, phase 2, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and pregabalin‐controlled, dose‐finding study of DS‐5565 in patients with pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01504412 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 5 January 2012). [CTG: NCT01504412; Daiichi Sankyo : DS5565‐A‐J202]
NCT01688947 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01688947. A phase 2, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study evaluating the analgesic efficacy and safety of V116517 in subjects with moderate to severe chronic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01688947 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 20 September 2012). [CTG: NCT01688947; VND2002]
NCT01939366 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01939366. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of multiple doses of oral cebranopadol in subjects with moderate to severe chronic pain due to diabetic peripheral neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01939366 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 11 September 2013). [CTG: NCT01939366]
NCT02927951 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02927951. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, cross‐over study on the effect of pregabalin on pain related to walking in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02927951 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 7 October 2016). [CTG: NCT02927951]
References to ongoing studies
NCT01869569 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01869569. Effect of pregabalin in patients with radiation‐induced peripheral neuropathic pain: a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01869569 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 5 June 2013). [2012026; NCT01869569; Sun Yat‐sen Memorial Hospital: SYSN00]
NCT02394951 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02394951. Investigation of somatosensory predictors of response to pregabalin in painful chemotherapy‐induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02394951 (accessed 12 June 2017) (first posted 20 March 2015). [CTG: NCT02394951]
NCT02417935 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02417935. A Japan post‐marketing, randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group, flexible dose comparative study to assess the non‐inferiority of duloxetine compared with pregabalin in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02417935 (accessed 12 June 2017) (first posted 16 April 2015). [CTG: NCT02417935; Eli Lilly: F1J‐JE‐HMHA; 14378]
NCT02607254 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02607254. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin in treatment of neuropathic pain in patients with idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02607254 (accessed 18 February 2018) (first posted 18 November 2015). [CTG: NCT02607254]
NCT02868801 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02868801. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin sustained release tablet for postherpetic neuralgia ‐ a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02868801 (accessed 13 February 2018) (first posted 16 August 2016). [CTG: NCT02868801; HRPRBL‐PHN]
NCT03276689 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT03276689. 'Fix the Dysfunction' concept for mechanism‐based pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain by drug. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03276689 (accessed 2 May 2018) (first posted 8 September 2017). [0381‐16‐RMB_CTIL; NCT03276689]
Additional references
AlBalawi 2013
Baron 2012
Baron 2017
Berger 2004
Berger 2009
Berger 2012
Bouhassira 2008
-
- Bouhassira D, Lantéri‐Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008;136(3):380‐7. - PubMed
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive ‐ trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. [DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn188] - DOI - PubMed
Calvo 2012
Chaparro 2012
Colloca 2017
de Guglielmo 2013
Dechartres 2013
Dechartres 2014
Demant 2014
-
- Demant DT, Lund K, Vollert J, Maier C, Segerdahl M, Finnerup NB, et al. The effect of oxcarbazepine in peripheral neuropathic pain depends on pain phenotype: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phenotype‐stratified study. Pain 2014;155(11):2263‐73. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.08.014] - DOI - PubMed
Derry 2012
Derry 2014
Derry 2016a
Derry 2016b
Derry 2017
Dworkin 2008
Dworkin 2013
Edwards 1999
Edwards 2004
Eipe 2015
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
EMC 2017
-
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. emc.medicines.org.uk/ (accessed 13 February 2017).
EPOC 2015
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). 23. Worksheets for preparing a Summary of Findings using GRADE. Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors (accessed 13 February 2017).
Evoy 2017
Fanelli 2017
Finnerup 2013
Finnerup 2015
Freeman 2015
Gaskell 2014
Gaskell 2016
Gurusamy 2014
Gustorff 2008
Guyatt 2011
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:151‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006] - DOI - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
Hall 2008
Helfert 2015
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hoffman 2010
Ioannidis 2001
-
- Ioannidis JP, Lau J. Completeness of safety reporting in randomized trials: an evaluation of 7 medical areas. Journal of the American Medical Association 2001;285(4):437‐43. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Jensen 2011
Jensen 2012
-
- Jensen MP, Hsu PH, Vanhove GF. Early pain reduction can predict treatment response: results of integrated efficacy analyses of a once‐daily gastroretentive formulation of gabapentin in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Medicine 2012;13(8):1059‐66. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2012.01427.x.] - DOI - PubMed
Kalso 2013
Karabis 2016
-
- Karabis A, Nikolakopoulos S, Pandhi S, Papadimitropoulou K, Nixon R, Chaves RL, et al. High correlation of VAS pain scores after 2 and 6 weeks of treatment with VAS pain scores at 12 weeks in randomised controlled trials in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: meta‐analysis and implications. Arthritis Research and Therapy 2016;18:73. [DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0972-7] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Katusic 1991
-
- Katusic S, Williams DB, Beard CM, Bergstralh EJ, Kurland LT. Epidemiology and clinical features of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: similarities and differences, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945‐1984. Neuroepidemiology 1991;10(5‐6):276‐81. [DOI: 10.1159/000110284] - DOI - PubMed
Khan 1996
-
- Khan KS, Daya S, Collins JA, Walter SD. Empirical evidence of bias in infertility research: overestimation of treatment effect in crossover trials using pregnancy as the outcome measure. Fertility and Sterility 1996;65(5):939‐45. - PubMed
Koopman 2009
L'Abbé 1987
Liébana‐Hermoso 2018
Loke 2001
Lunn 2014
McQuay 1995
McQuay 2007
-
- McQuay HJ, Smith LA, Moore RA. Chronic pain. In: Stevens A, Raftery J, Mant J, Simpson S editor(s). Health Care Needs Assessment: The Epidemiologically Based Needs Assessment Reviews: Third Series. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishing, 2007. [ISBN: 978‐1‐84619‐063‐6]
McQuay 2008
Moher 1999
-
- Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of reporting of meta‐analyses. Lancet 1999;354:1896‐900. - PubMed
Moore 1998
Moore 2005
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15‐23. [ISBN: 978‐0‐931092‐69‐5]
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. ACTINPAIN Writing Group of the IASP Special Interest Group on Systematic Reviews in Pain Relief, Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Systematic Review Group Editors. "Evidence" in chronic pain ‐ establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.011] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
Moore 2010d
Moore 2010e
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.107805] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2010f
-
- Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Straube S, Aldington D, Wiffen P, et al. for the ACTINPAIN Writing Group of the IASP Special Interest Group (SIG) on Systematic Reviews in Pain Relief. Clinical effectiveness: an approach to clinical trial design more relevant to clinical practice, acknowledging the importance of individual differences. Pain 2010;149(2):173‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.007] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2011b
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.030] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2012a
Moore 2012b
Moore 2013a
Moore 2013b
Moore 2013c
Moore 2014a
Moore 2014b
Moore 2015a
Moore 2015b
Moore 2015c
Moulin 2014
Nguyen 2017
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Neuropathic pain ‐ pharmacological management: the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in adults in non‐specialist settings, 2013. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg173 (accessed 13 February 2017). - PubMed
Nüesch 2010
O'Brien 2010
PaPaS 2012
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group. PaPaS Author and Referee Guidance. papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 7 February 2017).
Patel 2016
PCA 2018
-
- NHS Digital. Prescription Cost Analysis England 2017. NHS Digital, part of the Government Statistical Service, 8 March 2018. [ISBN: 978‐1‐78386‐981‐7]
Perloff 2011
Pharmacompass 2018
-
- Pharmacompass. Pregabalin suppliers listed on PharmaCompass. www.pharmacompass.com/listed‐active‐pharmaceutical‐ingredients/pregabalin (accessed 21 May 2018).
PharmaMarketing 2017
-
- Pharma Marketing. Top 50 pharmaceutical products by global sales. http://www.pmlive.com/top_pharma_list/Top_50_pharmaceutical_products_by_... (accessed 29 June 2017).
Quintero 2017
Rappaport 1994
-
- Rappaport ZH, Devor M. Trigeminal neuralgia: the role of self‐sustaining discharge in the trigeminal ganglion. Pain 1994;56:127‐38. - PubMed
Rauck 2013c
-
- Rauck RL, Irving GA, Wallace MS, Vanhove GF, Sweeney M. Once‐daily gastroretentive gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia: integrated efficacy, time to onset of pain relief and safety analyses of data from two phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled studies. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2013;46(2):219‐28. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.07.011] - DOI - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5. Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roberts 2015
Schjerning 2016
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Scott 2006
Seers 2018
SIGN 2013
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN Guideline 136 ‐ Management of chronic pain. 2013. sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/136/contents.html (accessed 1 March 2017).
Smalldone 2004
Soni 2013
Stannard 2016
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrolment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Sultan 2008
Thorlund 2011
Torrance 2006
-
- Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ. The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. Journal of Pain 2006;7(4):281‐9. - PubMed
Tramèr 1997
Treede 2008
Turner 2013
van Hecke 2014
van Hoek 2009
von Hehn 2012
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wiffen 2013
Wiffen 2015
Wiffen 2016
Wiffen 2017a
References to other published versions of this review
Moore 2009
Wiffen 2000
Wiffen 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

