CD69+ memory T lymphocytes of the bone marrow and spleen express the signature transcripts of tissue-resident memory T lymphocytes
- PMID: 30673129
- PMCID: PMC6563480
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201847982
CD69+ memory T lymphocytes of the bone marrow and spleen express the signature transcripts of tissue-resident memory T lymphocytes
Abstract
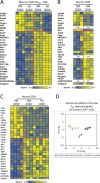
It is a matter of current debate whether the bone marrow is a hub for circulating memory T lymphocytes and/or the home of resident memory T lymphocytes. Here we demonstrate for CD69+ murine CD8+ , and CD69+ murine and human CD4+ memory T lymphocytes of the bone marrow, making up between 30 and 60% of bone marrow memory T lymphocytes, that they express the gene expression signature of tissue-resident memory T lymphocytes. This suggests that a substantial proportion of bone marrow memory T lymphocytes are resident. It adds to previous evidence that bone marrow memory T cells are resting in terms of mobility and proliferation, and maintain exclusive long-term memory to distinct, systemic antigens.
Keywords: Bone marrow; CD69; Memory T cells; Spleen; Tissue-resident signature genes.
© 2019 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tokoyoda, K. et al., Immunity 2009. 30: 721–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

