Structural Basis of Karrikin and Non-natural Strigolactone Perception in Physcomitrella patens
- PMID: 30673608
- PMCID: PMC7233462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.003
Structural Basis of Karrikin and Non-natural Strigolactone Perception in Physcomitrella patens
Abstract
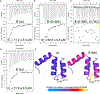
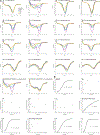
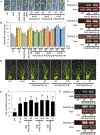
In plants, strigolactones are perceived by the dual receptor-hydrolase DWARF14 (D14). D14 belongs to the superfamily of α/β hydrolases and is structurally similar to the karrikin receptor KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE 2 (KAI2). The moss Physcomitrella patens is an ideal model system for studying this receptor family, because it includes 11 highly related family members with unknown ligand specificity. We present the crystal structures of three Physcomitrella D14/KAI2-like proteins and describe a loop-based mechanism that leads to a permanent widening of the hydrophobic substrate gorge. We have identified protein clades that specifically perceive the karrikin KAR1 and the non-natural strigolactone isomer (-)-5-deoxystrigol in a highly stereoselective manner.
Keywords: Physcomitrella patens; karrikin; strigolactone; α/β hydrolases.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama K, Matsuzaki K, and Hayashi H. (2005). Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 435, 824–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

