Clinical performance of Anyplex II HPV28 by human papillomavirus type and viral load in a referral population
- PMID: 30673759
- PMCID: PMC6343909
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210997
Clinical performance of Anyplex II HPV28 by human papillomavirus type and viral load in a referral population
Abstract
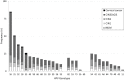
Anyplex II HPV28 (`Anyplex`) is a semi-quantitative DNA PCR assay divided into set A, comprising 14 high risk (hr)HPV types; and set B, comprising 5 possibly hrHPV types and 9 low risk (lr)HPV types. We compared the ability of Anyplex to that of Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2) and PreTect HPV-Proofer (`Proofer`) to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade two or worse (CIN2+) by HPV types and viral load. This cross-sectional study included 296 women referred to colposcopy with abnormal cervical cytology and/or persistent HPV infection. CIN2+ was identified in 175/296 women. Liquid based cytology samples were used to perform HPV testing. The sensitivity of Anyplex to detect CIN2+ was 98.9% (95% CI 95.9-99.9) and specificity 43.0% (95% CI 34.0-52.3). Restricting to medium and high viral loads in Anyplex set A, sensitivity and specificity were 97.1% (95% CI 93.5-99.1) and 59.5% (95% CI 50.2-68.3) with positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) 77.6% and 93.5%, respectively, comparable to HC2. Restricting Anyplex to the hrHPV types in Proofer, HPV16, 18, 31, 33 and 45, sensitivity and specificity for CIN2+ were 85.1% (95% CI 79.0-90.1) and 71.1% (95% CI 62.1-79.0), comparable to Proofer`s. When adding HPV52 and 58, the sensitivity for CIN2+ was 92.6% (95% CI 87.6-96.0) and CIN3+ 96.5% (95% CI 92.0-98.8). No value of Anyplex set B was found in detecting CIN2+. In conclusion, the clinical performance of medium and high viral loads in Anyplex set A was comparable to HC2. Restricting the test to the 7 hrHPV types included in the 9-valent HPV-vaccine, HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58, satisfies the international criteria for cervical cancer screening with relative sensitivity compared to HC2 for CIN2+ and CIN3+ of 0.98 and 1.01, respectively. Detecting all 28 Anyplex HPV types adds no benefit in a referral population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- IARC. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol 100B, p. 255–296 Lyon: IARC; 2012 [cited 2018 03.09.]. https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100B-11.pdf.
-
- Meijer CJ, Berkhof H, Heideman DA, Hesselink AT, Snijders PJ. Validation of high-risk HPV tests for primary cervical screening. J Clin Virol. 2009;46 Suppl 3:S1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

