Nanoparticle-Integrated Hydrogels as Multifunctional Composite Materials for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 30674171
- PMCID: PMC6318588
- DOI: 10.3390/gels1020162
Nanoparticle-Integrated Hydrogels as Multifunctional Composite Materials for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
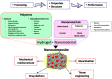
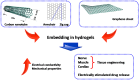
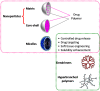
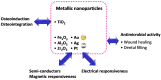
This review focuses on the most recent developments in the field of nanocomposite hydrogels intended for biomedical applications. Nanocomposite hydrogels are hydrated polymeric networks with a physically or covalently crosslinked three-dimensional (3D) structure swollen with water, in the presence of nanoparticles or nanostructures. A wide array of nanomaterials (polymeric, carbon-based, metallic, ceramic) can be incorporated within the hydrogel network to obtain reinforced nanocomposite hydrogels. Nanocomposites represent a new class of materials with properties absent in the individual components. In particular, the incorporation of nanomaterials within a polymeric hydrogel network is an attractive approach to tailor the mechanical properties of the hydrogels and/or to provide the nanocomposite with responsiveness to external stimuli.
Keywords: biomedical applications; hydrogels; nanocomposite hydrogels; nanocomposites; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Biondi M., Ungaro F., Quaglia F., Netti P.A. Controlled drug delivery in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008;60:229–242. - PubMed
-
- Vashist A., Gupta Y.K., Ahmad S. Recent advances in hydrogel based drug delivery systems for the human body. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2014;2:147–166. - PubMed
-
- Mollica F., Biondi M., Muzzi S., Ungaro F., Quaglia F., La Rotonda M.I., Netti P.A. Mathematical modelling of the evolution of protein distribution within single PLGA microspheres: prediction of local concentration profiles and release kinetics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008;19:1587–1593. doi: 10.1007/s10856-007-3301-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ungaro F., Biondi M., d’Angelo I., Indolfi L., Quaglia F., Netti P.A., La Rotonda M.I. Microsphere-integrated collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering: effect of microsphere formulation and scaffold properties on protein release kinetics. J. Control. Release. 2006;113:128–136. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

