Immune regulation by glucocorticoids can be linked to cell type-dependent transcriptional responses
- PMID: 30674564
- PMCID: PMC6363437
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180595
Immune regulation by glucocorticoids can be linked to cell type-dependent transcriptional responses
Abstract
Glucocorticoids remain the most widely used immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory drugs, yet substantial gaps exist in our understanding of glucocorticoid-mediated immunoregulation. To address this, we generated a pathway-level map of the transcriptional effects of glucocorticoids on nine primary human cell types. This analysis revealed that the response to glucocorticoids is highly cell type dependent, in terms of the individual genes and pathways affected, as well as the magnitude and direction of transcriptional regulation. Based on these data and given their importance in autoimmunity, we conducted functional studies with B cells. We found that glucocorticoids impair upstream B cell receptor and Toll-like receptor 7 signaling, reduce transcriptional output from the three immunoglobulin loci, and promote significant up-regulation of the genes encoding the immunomodulatory cytokine IL-10 and the terminal-differentiation factor BLIMP-1. These findings provide new mechanistic understanding of glucocorticoid action and emphasize the multifactorial, cell-specific effects of these drugs, with potential implications for designing more selective immunoregulatory therapies.
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Figures





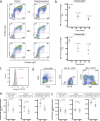
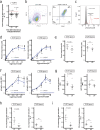
Comment in
-
Glucocorticoid response mapped.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 Apr;15(4):189. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0191-0. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30824878 No abstract available.
References
-
- Altonsy M.O., Sasse S.K., Phang T.L., and Gerber A.N.. 2014. Context-dependent cooperation between nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and the glucocorticoid receptor at a TNFAIP3 intronic enhancer: a mechanism to maintain negative feedback control of inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 289:8231–8239. 10.1074/jbc.M113.545178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartholome B., Spies C.M., Gaber T., Schuchmann S., Berki T., Kunkel D., Bienert M., Radbruch A., Burmester G.R., Lauster R., et al. 2004. Membrane glucocorticoid receptors (mGCR) are expressed in normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and up-regulated after in vitro stimulation and in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. FASEB J. 18:70–80. 10.1096/fj.03-0328com - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., and Hochberg Y.. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

