Balancing trade-offs between biotic and abiotic stress responses through leaf age-dependent variation in stress hormone cross-talk
- PMID: 30674663
- PMCID: PMC6369802
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1817233116
Balancing trade-offs between biotic and abiotic stress responses through leaf age-dependent variation in stress hormone cross-talk
Abstract
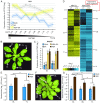
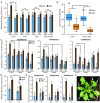
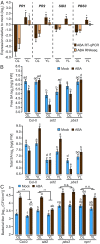
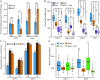
In nature, plants must respond to multiple stresses simultaneously, which likely demands cross-talk between stress-response pathways to minimize fitness costs. Here we provide genetic evidence that biotic and abiotic stress responses are differentially prioritized in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves of different ages to maintain growth and reproduction under combined biotic and abiotic stresses. Abiotic stresses, such as high salinity and drought, blunted immune responses in older rosette leaves through the phytohormone abscisic acid signaling, whereas this antagonistic effect was blocked in younger rosette leaves by PBS3, a signaling component of the defense phytohormone salicylic acid. Plants lacking PBS3 exhibited enhanced abiotic stress tolerance at the cost of decreased fitness under combined biotic and abiotic stresses. Together with this role, PBS3 is also indispensable for the establishment of salt stress- and leaf age-dependent phyllosphere bacterial communities. Collectively, our work reveals a mechanism that balances trade-offs upon conflicting stresses at the organism level and identifies a genetic intersection among plant immunity, leaf microbiota, and abiotic stress tolerance.
Keywords: combined stress; microbiota; phytohormone; plant fitness; stress trade-off.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pieterse CM, Leon-Reyes A, Van der Ent S, Van Wees SC. Networking by small-molecule hormones in plant immunity. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:308–316. - PubMed
-
- Bostock RM, Pye MF, Roubtsova TV. Predisposition in plant disease: Exploiting the nexus in abiotic and biotic stress perception and response. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2014;52:517–549. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, et al. Dual function of Arabidopsis ATAF1 in abiotic and biotic stress responses. Cell Res. 2009;19:1279–1290. - PubMed
-
- Berens ML, Berry HM, Mine A, Argueso CT, Tsuda K. Evolution of hormone signaling networks in plant defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2017;55:401–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

