Optofluidic real-time cell sorter for longitudinal CTC studies in mouse models of cancer
- PMID: 30674677
- PMCID: PMC6369805
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1814102116
Optofluidic real-time cell sorter for longitudinal CTC studies in mouse models of cancer
Abstract
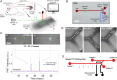
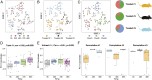
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) play a fundamental role in cancer progression. However, in mice, limited blood volume and the rarity of CTCs in the bloodstream preclude longitudinal, in-depth studies of these cells using existing liquid biopsy techniques. Here, we present an optofluidic system that continuously collects fluorescently labeled CTCs from a genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) for several hours per day over multiple days or weeks. The system is based on a microfluidic cell sorting chip connected serially to an unanesthetized mouse via an implanted arteriovenous shunt. Pneumatically controlled microfluidic valves capture CTCs as they flow through the device, and CTC-depleted blood is returned back to the mouse via the shunt. To demonstrate the utility of our system, we profile CTCs isolated longitudinally from animals over 4 days of treatment with the BET inhibitor JQ1 using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) and show that our approach eliminates potential biases driven by intermouse heterogeneity that can occur when CTCs are collected across different mice. The CTC isolation and sorting technology presented here provides a research tool to help reveal details of how CTCs evolve over time, allowing studies to credential changes in CTCs as biomarkers of drug response and facilitating future studies to understand the role of CTCs in metastasis.
Keywords: GEMM; circulating tumor cells; metastasis; microfluidic; single-cell RNA-Seq.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pantel K, Speicher MR. The biology of circulating tumor cells. Oncogene. 2016;35:1216–1224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007287/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 GM119419/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM087237/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI039671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI118672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG006193/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA202820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA170592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA217377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA184956/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

