Viral population analysis of the taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus, by using Batch Learning Self-Organizing Maps and BLAST search
- PMID: 30674747
- PMCID: PMC6451905
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.18-0483
Viral population analysis of the taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus, by using Batch Learning Self-Organizing Maps and BLAST search
Abstract
Ticks transmit a wide range of viral, bacterial, and protozoal pathogens, which are often zoonotic. Several novel tick-borne viral pathogens have been reported during the past few years. The aim of this study was to investigate a diversity of tick viral populations, which may contain as-yet unidentified viruses, using a combination of high throughput pyrosequencing and Batch Learning Self-Organizing Map (BLSOM) program, which enables phylogenetic estimation based on the similarity of oligonucleotide frequencies. DNA/cDNA prepared from virus-enriched fractions obtained from Ixodes persulcatus ticks was pyrosequenced. After de novo assembly, contigs were cataloged by the BLSOM program. In total 41 different viral families and order including those previously associated with human and animal diseases such as Bunyavirales, Flaviviridae, and Reoviridae, were detected. Therefore, our strategy is applicable for viral population analysis of other arthropods of medical and veterinary importance, such as mosquitos and lice. The results lead to the contribution to the prediction of emerging tick-borne viral diseases. A sufficient understanding of tick viral populations will also empower to analyze and understand tick biology including vector competency and interactions with other pathogens.
Keywords: Batch Learning Self-Organizing Map; Ixodes persulcatus; high throughput pyrosequencing; viral population analysis.
Figures
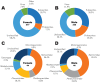

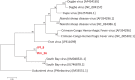
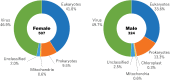
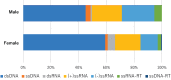
References
-
- Belhouchet M., Mohd Jaafar F., Tesh R., Grimes J., Maan S., Mertens P. P., Attoui H.2010. Complete sequence of Great Island virus and comparison with the T2 and outer-capsid proteins of Kemerovo, Lipovnik and Tribec viruses (genus Orbivirus, family Reoviridae). J. Gen. Virol. 91: 2985–2993. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.024760-0 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

