The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch is required for B-cell development
- PMID: 30674954
- PMCID: PMC6344599
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36844-9
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch is required for B-cell development
Abstract
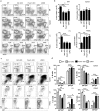
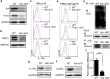
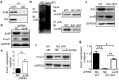
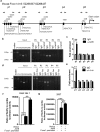
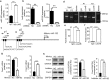
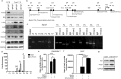
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch interacts with Foxo1 and targets it for ubiquitination and degradation during follicular helper T-cell differentiation, whereas the transcription factor Foxo1 plays a critical role in B-cell development. Thus, we proposed that Itch mediates B-cell differentiation. Unexpectedly, we found that Itch deficiency downregulated Foxo1 expression in B cells. Itch cKO (conditional knock out in B cells) mice had fewer pro-B cells in the bone marrow, more small resting IgM-IgD-B cells in the periphery, and lower B-cell numbers in the lymph nodes through decreased Foxo1-mediated IL-7Rα, RAG, and CD62L expression, respectively. Importantly, Itch deficiency reduced Foxo1 mRNA expression by up-regulating JunB-mediated miR-182. Finally, Foxo1 negatively regulated JunB expression by up-regulating Itch. Thus, we have identified a novel regulatory axis between Itch and Foxo1 in B cells, suggesting that Itch is essential for B-cell development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Roquin Suppresses the PI3K-mTOR Signaling Pathway to Inhibit T Helper Cell Differentiation and Conversion of Treg to Tfr Cells.Immunity. 2017 Dec 19;47(6):1067-1082.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 29246441
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch is required for the differentiation of follicular helper T cells.Nat Immunol. 2014 Jul;15(7):657-66. doi: 10.1038/ni.2912. Epub 2014 May 25. Nat Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24859451 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of Ikaros cripples expression of Foxo1 and its targets in naive T cells.Immunology. 2017 Nov;152(3):494-506. doi: 10.1111/imm.12786. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28670688 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch in T cell activation, differentiation, and tolerance.Semin Immunol. 2007 Jun;19(3):197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17433711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of autoimmune disease by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch.Cell Immunol. 2019 Jun;340:103916. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Cell Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31126634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ITCH as a potential therapeutic target in human cancers.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Dec;67(Pt 2):117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 32165318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch restricts antigen-driven B cell responses.J Exp Med. 2019 Sep 2;216(9):2170-2183. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181953. Epub 2019 Jul 16. J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31311822 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin Ligase Itch Skews Light Zone Selection in Germinal Centers.J Immunol. 2023 May 15;210(10):1473-1481. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200824. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36929899 Free PMC article.
-
TET2 Regulates 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signature and CD4+ T-Cell Balance in Allergic Rhinitis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022 Mar;14(2):254-272. doi: 10.4168/aair.2022.14.2.254. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35255541 Free PMC article.
-
Itch regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses in mice and humans.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Jul;108(1):353-362. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR0320-272R. Epub 2020 Apr 30. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32356405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abolhassani H, Parvaneh N, Rezaei N, Hammarstrom L, Aghamohammadi A. Genetic defects in B-cell development and their clinical consequences. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2014;24:6–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

