Deciphering the Potential Pharmaceutical Mechanism of GUI-ZHI-FU-LING-WAN on Systemic Sclerosis based on Systems Biology Approaches
- PMID: 30674993
- PMCID: PMC6344516
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36314-2
Deciphering the Potential Pharmaceutical Mechanism of GUI-ZHI-FU-LING-WAN on Systemic Sclerosis based on Systems Biology Approaches
Abstract
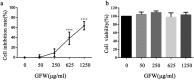
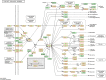
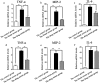
Systemic sclerosis (SSc; scleroderma) is a complicated idiopathic connective tissue disease with seldom effective treatment. GUI-ZHI-FU-LING-WAN (GFW) is a classic Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formula widely used for the treatment of SSc. However, the mechanism of how the GFW affects SSc remains unclear. In this study, the system biology approach was utilized to analyze herb compounds and related targets to get the general information of GFW. The KEGG enrichment analysis of 1645 related targets suggested that the formula is involved in the VEGF signaling pathway, the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, etc. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of the relationship among the 3 subsets (formula targets, drug targets and disease genes) showed that the formula targets overlapped with 38.0% drug targets and 26.0% proteins encoded by disease genes. Through the analysis of SSc related microarray statistics from the GEO database, we also validated the consistent expression behavior among the 3 subsets before and after treatment. To further reveal the mechanism of prescription, we constructed a network among 3 subsets and decomposed it into 24 modules to decipher how GFW interfere in the progress of SSc. The modules indicated that the intervention may come into effect through following pathogenic processes: vasculopathy, immune dysregulation and tissue fibrosis. Vitro experiments confirmed that GFW could suppress the proliferation of fibroblasts and decrease the Th1 cytokine (TNF-α, MIP-2 and IL-6) expression for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and bleomycin (BLM) stimulation in macrophages, which is consistent with previous conclusion that GFW is able to relieve SSc. The systems biology approach provides a new insight for deepening understanding about TCM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring the mechanisms of Gui Zhi Fu Ling Wan on varicocele via network pharmacology and molecular docking.Andrologia. 2022 Dec;54(11):e14635. doi: 10.1111/and.14635. Epub 2022 Nov 13. Andrologia. 2022. PMID: 36372090 Free PMC article.
-
A Systems Biology-Based Investigation into the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Sheng-ma-bie-jia-tang Acting on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Multi-Level Data Integration.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 12;5:16401. doi: 10.1038/srep16401. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26560501 Free PMC article.
-
Gui-zhi-fu-ling-wan alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ferroptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1552251. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1552251. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308766 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Mechanisms of Guizhi Fuling Wan in Treating Endometriosis: An Analysis Based on TCMSP and DisGeNET Databases.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jul 15;329:118190. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118190. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38614264 Review.
-
[Thoughts and exploration on studying pharmacological mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine using network biology approach].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Jan;37(2):146-51. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22737841 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
One of the active ingredients in Paeoniae Radix Alba functions as JAK1 inhibitor in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 19;13:906763. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.906763. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36199685 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Mechanism and Application of Keishibukuryogan.Front Nutr. 2021 Dec 24;8:760918. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.760918. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35004802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Care patterns and Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution as factors of depression and anxiety in patients with systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study during the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Integr Neurosci. 2023 Feb 14;17:1052683. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2023.1052683. eCollection 2023. Front Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36864895 Free PMC article.
-
Global research status and trends of interactions between Traditional Chinese medicine and pulmonary fibrosis: A new dawn in treatment.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34592. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34592. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39149021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Formulations: Novel Viewpoint for Scleroderma Adjunct Treatment.J Immunol Res. 2021 Jun 24;2021:9920416. doi: 10.1155/2021/9920416. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34258301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pellar, R. E. & Pope, J. E. Evidence-based management of systemic sclerosis: Navigating recommendations and guidelines. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.12.003 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

