Enhanced noninvasive imaging of oncology models using the NIS reporter gene and bioluminescence imaging
- PMID: 30674994
- PMCID: PMC7170803
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-019-0081-2
Enhanced noninvasive imaging of oncology models using the NIS reporter gene and bioluminescence imaging
Abstract
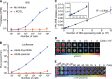
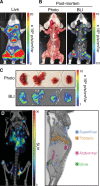
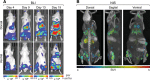
Noninvasive bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of luciferase-expressing tumor cells has advanced pre-clinical evaluation of cancer therapies. Yet despite its successes, BLI is limited by poor spatial resolution and signal penetration, making it unusable for deep tissue or large animal imaging and preventing precise anatomical localization or signal quantification. To refine pre-clinical BLI methods and circumvent these limitations, we compared and ultimately combined BLI with tomographic, quantitative imaging of the sodium iodide symporter (NIS). To this end, we generated tumor cell lines expressing luciferase, NIS, or both reporters, and established tumor models in mice. BLI provided sensitive early detection of tumors and relatively easy monitoring of disease progression. However, spatial resolution was poor, and as the tumors grew, deep thoracic tumor signals were massked by overwhelming surface signals from superficial tumors. In contrast, NIS-expressing tumors were readily distinguished and precisely localized at all tissue depths by positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging. Furthermore, radiotracer uptake for each tumor could be quantitated noninvasively. Ultimately, combining BLI and NIS imaging represented a significant enhancement over traditional BLI, providing more information about tumor size and location. This combined imaging approach should facilitate comprehensive evaluation of tumor responses to given therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
RV, LS, KWP are employees of Imanis. KW, SJR, Imanis Life Sciences, and Mayo Clinic have a financial interest in the NIS technology used in this paper. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang Y, Tseng JC, Sun Y, Beck AH, Kung AL. Noninvasive imaging of tumor burden and molecular pathways in mouse models of cancer. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015;2015:135–44. - PubMed
-
- James ML, Gambhir SS. A molecular imaging primer: modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:897–965. - PubMed
-
- O’Neill K, Lyons SK, Gallagher WM, Curran KM, Byrne AT. Bioluminescent imaging: a critical tool in pre-clinical oncology research. J Pathol. 2010;220:317–27. - PubMed
-
- Baker M. Whole-animal imaging: the whole picture. Nature. 2010;463:977–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

