Drainage During Endoscopic Thyroidectomy
- PMID: 30675096
- PMCID: PMC6333566
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2018.00060
Drainage During Endoscopic Thyroidectomy
Abstract
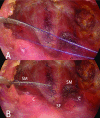
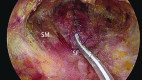
Background: Conventional cervical drainage tubes are placed crossing the suprasternal fossa during endoscopic thyroidectomy. In our clinical experience, some patients show shallow or absent suprasternal fossa, which affects the cosmetic outcome in the patient. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the feasibility and significance of restoring the suprasternal fossa by changing the position of neck drainage tubes.
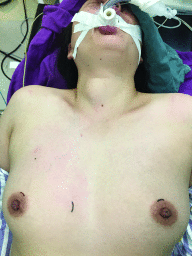
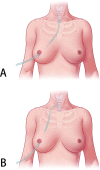
Methods and materials: A total of 117 female patients were enrolled and divided into 2 groups, including 59 and 58 individuals in the Conventional (conventional anterior neck region negative pressure drainage) and Improvement (improved method with a negative pressure drainage) groups. Then, restoration of the suprasternal fossa in all subjects was observed at 1 day postsurgery, the day of extubation, and 3 months postoperatively. In addition, drainage volume, the time to extubation, and abnormal neck sensations were compared between the groups.
Results: Compared with the Conventional group, the Improvement group showed improved restoration of the suprasternal fossa, with the patients more satisfied with the cosmetic outcome. However, operation time, postoperative drainage volume, and extubation time were not significantly different between the 2 groups.
Conclusions: In endoscopic thyroidectomy via the chest and breast approach, using the new drainage technique described here could yield improved restoration of the suprasternal fossa, ameliorating the cosmetic outcome and patient satisfaction.
Keywords: Aesthetics; Drainage tube; Endoscopy; Suprasternal fossa; Thyroid.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transareola single-site endoscopic thyroidectomy: clinical study of 28 cases with thyroid nodules.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013 Jul;23(7):584-7. doi: 10.1089/lap.2012.0386. Epub 2013 May 7. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013. PMID: 23651142
-
How Should the Surgical Approach In Thyroidectomy Be Selected? A Prospective Study Comparing the Trauma of 3 Different Thyroidectomy Surgical Approaches.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2020 Feb;30(1):22-25. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000743. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2020. PMID: 31855923 Free PMC article.
-
Total endoscopic thyroidectomy via bilateral breast and ipsilateral axillary approach: a clinical feasibility study.J Craniofac Surg. 2014 May;25(3):738-41. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000721. J Craniofac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24657976
-
[Endoscopic thyroidectomy for solitary nodules].Ann Chir. 2003 Dec;128(10):696-701. doi: 10.1016/j.anchir.2003.10.016. Ann Chir. 2003. PMID: 14706880 Review. French.
-
What is the evidence for endoscopic thyroidectomy in the management of benign thyroid disease?World J Surg. 2008 Jul;32(7):1325-32. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9505-0. World J Surg. 2008. PMID: 18327525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drainage Tube Placement May Not Be Necessary During Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Bilateral Areola Approach: A Preliminary Report.Front Surg. 2022 Mar 10;9:860130. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.860130. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35356502 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effect of a New Surgical Medical Drain Anti-Dislodgement Fixation Patch and Fixation Method in Postoperative Thyroid Care: A Randomized Trial.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024 Dec 9;20:837-847. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S491307. eCollection 2024. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 39677355 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for increased drain output after endoscopic thyroidectomy via areola approach: a retrospective cohort study.Gland Surg. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):2264-2273. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-360. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39822366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Byeon HK, Holsinger FC, Tufano RP, et al. Robotic total thyroidectomy with modified radical neck dissection via unilateral retroauricular approach. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(12):3872–3875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
