Metformin selectively targets 4T1 tumorspheres and enhances the antitumor effects of doxorubicin by downregulating the AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways
- PMID: 30675314
- PMCID: PMC6341857
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9827
Metformin selectively targets 4T1 tumorspheres and enhances the antitumor effects of doxorubicin by downregulating the AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways
Abstract
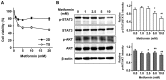
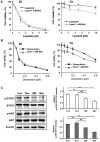
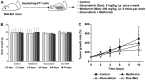
Recent studies have reported that metformin (Met), the first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, exhibited anticancer and chemoprotective effects in diverse cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the effects of Met on the drug-resistance of 4T1 murine breast cancer tumorspheres (TS) and the mechanism responsible for its drug-resistance. 4T1 TS exhibited accumulations of cells at the G0/G1 phase compared with cells in monolayer culture, which suggested the majority of cells in TS were quiescent. Furthermore, it was identified that activations of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathways in 4T1 TS conferred drug-resistance to doxorubicin (Dox) and lapatinib (Lapa). However, Met selectively targeted TS rather than cells in monolayer culture and increased the cytotoxic effect of Dox on TS by inhibiting activations of the STAT3 and AKT signaling pathways. These observations suggested that inhibitions of STAT3 and AKT underlie the selective cytotoxic effects of Met on TS. In addition, Met exhibited synergistic antitumor effects with Dox on 4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice. Our findings suggest that combinations of Met and cytotoxic anticancer drugs may offer an advantage for treating drug-resistant breast cancer.
Keywords: 4T1 breast cancer cells; drug-resistance; metformin; quiescence; tumorspheres.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lapatinib sensitizes quiescent MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by inhibiting the expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein-1.Oncol Rep. 2015 Aug;34(2):884-90. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4047. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26063481
-
Lapatinib enhances the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin in MCF-7 tumorspheres by inhibiting the drug efflux function of ABC transporters.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 May;72:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26054673
-
Stat3/Oct-4/c-Myc signal circuit for regulating stemness-mediated doxorubicin resistance of triple-negative breast cancer cells and inhibitory effects of WP1066.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):339-348. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4399. Epub 2018 May 8. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29750424
-
JSI124 inhibits breast cancer cell growth by suppressing the function of B cells via the downregulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Oncol Lett. 2014 Aug;8(2):928-932. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2221. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25013518 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Delivery of Metformin Enhances the Antimultidrug Resistant Tumor Effect of Doxorubicin by Improving Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment.Mol Pharm. 2019 Jul 1;16(7):2966-2979. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00199. Epub 2019 May 30. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31095914
Cited by
-
Metformin alters therapeutic effects in the BALB/c tumor therapy model.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 28;21(1):629. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08354-x. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34044797 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of targeted therapy in combination with metformin on human breast cancer cell lines.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 2;22(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01446-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38167105 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-resident macrophages are major tumor-associated macrophage resources, contributing to early TNBC development, recurrence, and metastases.Commun Biol. 2023 Feb 3;6(1):144. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04525-7. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36737474 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin and Cancer, an Ambiguanidous Relationship.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 19;15(5):626. doi: 10.3390/ph15050626. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
