Tuberous sclerosis complex exhibits a new renal cystogenic mechanism
- PMID: 30675765
- PMCID: PMC6344348
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13983
Tuberous sclerosis complex exhibits a new renal cystogenic mechanism
Abstract
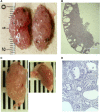
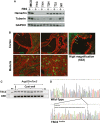
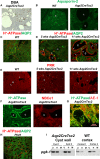
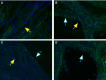
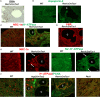
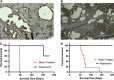
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a tumor predisposition syndrome with significant renal cystic and solid tumor disease. While the most common renal tumor in TSC, the angiomyolipoma, exhibits a loss of heterozygosity associated with disease, we have discovered that the renal cystic epithelium is composed of type A intercalated cells that have an intact Tsc gene that have been induced to exhibit Tsc-mutant disease phenotype. This mechanism appears to be different than that for ADPKD. The murine models described here closely resemble the human disease and both appear to be mTORC1 inhibitor responsive. The induction signaling driving cystogenesis may be mediated by extracellular vesicle trafficking.
Keywords: Intercalated cells; Tuberous sclerosis complex; renal cystic disease; renal cystogenesis.
© 2019 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Arulrajah, S. , Ertan G., Jordan L., Tekes A., Khaykin E., Izbudak I., et al. 2009. Magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion‐weighted imaging of normal‐appearing white matter in children and young adults with tuberous sclerosis complex. Neuroradiology 51:781–786. - PubMed
-
- Badenas, C. , Torra R., Perez‐Oller L., Mallolas J., Talbot‐Wright R., Torregrosa V., et al. 2000. Loss of heterozygosity in renal and hepatic epithelial cystic cells from ADPKD1 patients. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 8:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Benvenuto, G. , Li S., Brown S. J., Braverman R., Vass W. C., Cheadle J. P., et al. 2000. The tuberous sclerosis‐1 (TSC1) gene product hamartin suppresses cell growth and augments the expression of the TSC2 product tuberin by inhibiting its ubiquitination. Oncogene 19:6306–6316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

