Inkjet dispensing technologies: recent advances for novel drug discovery
- PMID: 30676831
- PMCID: PMC10357954
- DOI: 10.1080/17460441.2019.1567489
Inkjet dispensing technologies: recent advances for novel drug discovery
Abstract
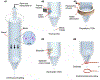
Inkjet-dispensing printing is a promising additive manufacturing method for pharmaceutical applications such as drug discovery. The unique advantages of this technology, including low cost, programmability, high resolution, high throughput, high speed, and biocompatibility, may reduce the financial resources needed to discover new drug candidates. Sophisticated and miniaturized assays have been developed to accomplish drug discovery and drug screening using modern inkjet dispensing printers. Areas covered: This paper reviews recent advancements in the field of inkjet printer technology for drug discovery. Various types of inkjet printers and their recent use for the drug discovery are summarized; physical and biological limitations of this technology are also examined. Furthermore, typical inks used in the inkjet printing technology are introduced. Expert opinion: Inkjet bioprinting technology is a promising tool for many biological and pharmaceutical applications. Several bottlenecks associated with this technology need to be addressed before commercialization. For example, sophisticated inks need to be synthesized to meet both biological and engineering restrictions. Further progress of parallel technologies will enhance the performance and functionality of the printers. It is also worth emphasizing that inkjet printing technologies must meet the requirement of regulatory agencies (e.g. the US Food & Drug Administration) for commercialization by the pharmaceutical industry.
Keywords: Inkjet dispensing technology; drug discovery; drug screening; ink; inkjet printer.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest:
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures




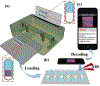
References
-
- Chameettachal S, Pati F. Inkjet-based 3D bioprinting. 3D Bioprinting in Regenerative Engineering:: Principles and Applications. 2018.
-
- Campbell PG, Miller ED, Fisher GW, et al. Engineered spatial patterns of FGF-2 immobilized on fibrin direct cell organization. Biomaterials. 2005;26(33):6762–6770. - PubMed
-
- Phillippi JA, Miller E, Weiss L, et al. Microenvironments engineered by inkjet bioprinting spatially direct adult stem cells toward muscle‐and bone‐like subpopulations. Stem cells. 2008;26(1):127–134. - PubMed
-
- Klebe RJ. Cytoscribing: a method for micropositioning cells and the construction of two-and three-dimensional synthetic tissues. Experimental cell research. 1988;179(2):362–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
