High dose hepatitis B vaccine is not effective in patients using immunomodulatory drugs: a pilot study
- PMID: 30676860
- PMCID: PMC6605832
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1574151
High dose hepatitis B vaccine is not effective in patients using immunomodulatory drugs: a pilot study
Abstract
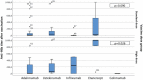
In patients undergoing immunotherapy, the quality of the immune response is reduced, which may negatively affect the efficacy of vaccination. This study was conducted in order to evaluate the efficacy of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccine in patients using immunomodulators. Seronegative patients for HBV who were using biological agents, were included in the study. The vaccination was administered on the standard schedule in 3 doses of 20 or 40 µg/ml. Eighty-two patients (52%) were males and the mean age of all patients was 44,8 ± 10,3 years. Among these 109 patients, 83 had psoriasis, 12 had Crohn's disease, six had rheumatoid arthritis, three had ulcerative colitis, three had hydradenitis supurativa, one had Behcet's disease and one had ankylosing spondylitis. The biological agents that were being used by these patients were adalimumab (62), ustekinumab (25), infliximab (12), etanercept (9) and golimumab (1). Seventy-three of the patients were vaccinated with a dose of 20 µg/ml and 36 with 40 µg/ml. The anti-HBs titers of fifty-eight (53.2%) patients were above 10 mIU/ml. The antibody response rate was lowest in infliximab-users (16.7%) (p = 0.007), which was followed by adalimumab (48.4%), and higher protection rates were achieved in patients using ustekinumab and etanercept (72% and 88.9%, respectively; p < 0.05). The HBV vaccine response rate in patients using immunomodulators was significantly lower than that in immunocompetent patients. Furthermore, high dose vaccination did not increase the response rate. Clinicians should take into account administering HBV vaccination before treatment with biological agent in patients who have negative HBV serology.
Keywords: Hepatitis B; high dose; immunomodulatory drugs; response; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B immunity and response to booster vaccination in children with inflammatory bowel disease treated with infliximab.Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan;107(1):133-8. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.295. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 21876562
-
Treatment with infliximab or azathioprine negatively impact the efficacy of hepatitis B vaccine in inflammatory bowel disease patients.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov;30(11):1591-5. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13001. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25967740
-
Antibody Response to Hepatitis B Virus Vaccine is Impaired in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease on Infliximab Therapy.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018 Jan 18;24(2):380-386. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izx001. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018. PMID: 29361083
-
Effects of immunosuppressants on immune response to vaccine in inflammatory bowel disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Mar 20;128(6):835-8. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.152683. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25758282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis-B Vaccine Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021 Oct 18;27(10):1610-1619. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaa353. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021. PMID: 33393585
Cited by
-
Uselessness of Serum p53 Antibody for Detecting Colitis-associated Cancer in the Era of Immunosuppressive Therapy.In Vivo. 2020 Mar-Apr;34(2):723-728. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11830. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32111776 Free PMC article.
-
An evidence-based guide to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination of patients on immunotherapies in dermatology.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Jun;84(6):1652-1666. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.01.047. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33482251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B vaccination associated with low response in patients with rheumatic diseases treated with biologics.RMD Open. 2023 Dec 6;9(4):e003597. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003597. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 38056920 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of Hepatitis B Vaccination in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis on Infliximab Is Attenuated Compared to Those on 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Therapies: A Prospective Observational Study.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;12(4):364. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040364. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675746 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on vaccine immunogenicity in patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 Oct;80(10):1255-1265. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221244. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 34493491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global hepatitis report 2017. Geneva; 2017 [accessed 2018 June] www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials