Enhanced activity of pyramidal neurons in the infralimbic cortex drives anxiety behavior
- PMID: 30677060
- PMCID: PMC6345483
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210949
Enhanced activity of pyramidal neurons in the infralimbic cortex drives anxiety behavior
Abstract
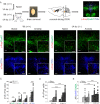
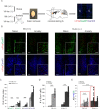
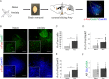
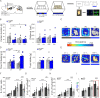
We show that in an animal model of anxiety the overall excitation, particularly in the infralimbic region of the medial prefrontal cortex (IL), is increased and that the activity ratio between excitatory pyramidal neurons and inhibitory interneurons (AR PN/IN) is shifted towards excitation. The same change in AR PN/IN is evident for wildtype mice, which have been exposed to an anxiety stimulus. We hypothesize, that an elevated activity and the imbalance of excitation (PN) and inhibition (IN) within the neuronal microcircuitry of the prefrontal cortex is responsible for anxiety behaviour and employed optogenetic methods in freely moving mice to verify our findings. Consistent with our hypothesis elevation of pyramidal neuron activity in the infralimbic region of the prefrontal cortex significantly enhanced anxiety levels in several behavioural tasks by shifting the AR PN/IN to excitation, without affecting motor behaviour, thus revealing a novel mechanism by which anxiety is facilitated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of GSK3β activation and modulation of synaptic plasticity by dopamine in 5-HT1A-receptor KO mice.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Feb;113(Pt A):124-136. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27678414
-
Bidirectional modulation of anxiety-related and social behaviors by amygdala projections to the medial prefrontal cortex.Neuroscience. 2016 May 3;321:197-209. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.041. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26204817 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chronic ethanol exposure on neuronal function in the prefrontal cortex and extended amygdala.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:735-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.06.017. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26188147 Free PMC article.
-
[An update on the conceptual and classification issues of anxiety, its neuroanatomy and problems of anxiolytic drug discovery].Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2015 Jun;17(2):69-80. Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. 2015. PMID: 26192900 Review. Hungarian.
-
Developing a neuronal model for the pathophysiology of schizophrenia based on the nature of electrophysiological actions of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Aug;21(2):161-94. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00112-2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10432466 Review.
Cited by
-
Long term effects of peripubertal stress on excitatory and inhibitory circuits in the prefrontal cortex of male and female mice.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Apr 1;14:100322. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100322. eCollection 2021 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 33869684 Free PMC article.
-
β2-Adrenoceptors in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Excitatory Neurons Regulate Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5578. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105578. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628393 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Involvement of Glutamatergic Neurons in the Anterior Insular Cortex for Subdiaphragmatic Vagotomy-induced Analgesia.Exp Neurobiol. 2023 Apr 30;32(2):68-82. doi: 10.5607/en23002. Exp Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37164647 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortex astrocytes modulate distinct neuronal populations to control anxiety-like behavior.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 21;16(1):7819. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63131-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40841557
-
Arhgap22 Disruption Leads to RAC1 Hyperactivity Affecting Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synapses and Cognition in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Dec;58(12):6092-6110. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02502-x. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34455539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jinks AL, McGregor IS. Modulation of anxiety-related behaviours following lesions of the prelimbic or infralimbic cortex in the rat. Brain Res. 1997;772: 181–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

