Which brain lesions produce spasticity? An observational study on 45 stroke patients
- PMID: 30677069
- PMCID: PMC6345431
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210038
Which brain lesions produce spasticity? An observational study on 45 stroke patients
Abstract
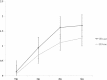
Spasticity is an important barrier that can hinder the restoration of function in stroke patients. Although several studies have attempted to elucidate the relationship between brain lesions and spasticity, the effects of specific brain lesions on the development of spasticity remain unclear. Thus, the present study investigated the effects of stroke lesions on spasticity in stroke patients. The present retrospective longitudinal observational study assessed 45 stroke patients using the modified Ashworth Scale to measure muscle spasticity. Each patient was assessed four times: initially (within 2 weeks of stroke) and at 1, 3, and 6 months after the onset of stroke. Brain lesions were analyzed using voxel-based lesion symptom mapping (VLSM) with magnetic resonance imaging images. Spasticity developed to a certain degree within 3 months in most stroke patients with spasticity. The VLSM method with non-parametric mapping revealed that lesions in the superior corona radiata, posterior limb of the internal capsule, posterior corona radiata, thalamus, putamen, premotor cortex, and insula were associated with the development of upper-limb spasticity. Additionally, lesions of the superior corona radiata, posterior limb of the internal capsule, caudate nucleus, posterior corona radiata, thalamus, putamen, and external capsule were associated with the development of lower-limb spasticity. The present study identified several brain lesions that contributed to post-stroke spasticity. Specifically, the involvement of white matter tracts and the striatum influenced the development of spasticity in the upper and lower limbs of stroke patients. These results may be useful for planning rehabilitation strategies and for understanding the pathophysiology of spasticity in stroke patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Lance JW. The control of muscle tone, reflexes, and movement: Robert Wartenberg Lecture. Neurology. 1980;30(12):1303–13. Epub 1980/12/01. . - PubMed
-
- Cramer SC, Nelles G, Benson RR, Kaplan JD, Parker RA, Kwong KK, et al. A functional MRI study of subjects recovered from hemiparetic stroke. Stroke. 1997;28(12):2518–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

