Deletion of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor and expression of the androgen receptor induce sarcomatoid carcinomas with signet ring cells in the mouse prostate
- PMID: 30677079
- PMCID: PMC6345450
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211153
Deletion of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor and expression of the androgen receptor induce sarcomatoid carcinomas with signet ring cells in the mouse prostate
Abstract
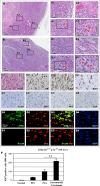
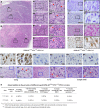
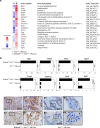
The tumor suppressor p16Ink4a, encoded by the INK4a gene, is an inhibitor of cyclin D-dependent kinases 4 and 6, CDK4 and CDK6. This inhibition prevents the phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), resulting in cellular senescence through inhibition of E2F-mediated transcription of S phase genes required for cell proliferation. The p16Ink4a plays an important role in tumor suppression, whereby its deletion, mutation, or epigenetic silencing is a frequently observed genetic alteration in prostate cancer. To assess its roles and related molecular mechanisms in prostate cancer initiation and progression, we generated a mouse model with conditional deletion of p16Ink4a in prostatic luminal epithelium. The mice underwent oncogenic transformation and developed prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) from eight months of age, but failed to develop prostatic tumors. Given the prevalence of aberrant androgen signaling pathways in prostate cancer initiation and progression, we then generated R26hARL/wt:p16L/L: PB-Cre4 compound mice, in which conditional expression of the human AR transgene and deletion of p16Ink4a co-occur in prostatic luminal epithelial cells. While R26hARL/wt:PB-Cre4 mice showed no visible pathological changes, R26hARL/wt:p16L/L: PB-Cre4 compound mice displayed an early onset of high-grade PIN (HGPIN), prostatic carcinoma, and metastatic lesions. Strikingly, we observed tumors resembling human sarcomatoid carcinoma with intermixed focal regions of signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) in the prostates of the compound mice. Further characterization of these tumors showed they were of luminal epithelial cell origin, and featured characteristics of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) with enhanced proliferative and invasive capabilities. Our results not only implicate a biological role for AR expression and p16Ink4a deletion in the pathogenesis of prostatic SRCC, but also provide a new and unique genetically engineered mouse (GEM) model for investigating the molecular mechanisms for SRCC development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The comprehensive role of E-cadherin in maintaining prostatic epithelial integrity during oncogenic transformation and tumor progression.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 28;15(10):e1008451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008451. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31658259 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of the Pten gene in the mouse prostate induces prostatic intraepithelial neoplasms at early ages but a slow progression to prostate tumors.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053476. Epub 2013 Jan 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308230 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of hepatocyte growth factor/MET signaling initiates oncogenic transformation and enhances tumor aggressiveness in the murine prostate.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 28;293(52):20123-20136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005395. Epub 2018 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30401749 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in mouse models of prostate cancer.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008 Jun 9;10:e16. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000689. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18538039 Review.
-
Prostatic signet-ring cell carcinoma: case report and literature review.Pathol Int. 1999 May;49(5):457-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00876.x. Pathol Int. 1999. PMID: 10417691 Review.
Cited by
-
The comprehensive role of E-cadherin in maintaining prostatic epithelial integrity during oncogenic transformation and tumor progression.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 28;15(10):e1008451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008451. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31658259 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant androgen action in prostatic progenitor cells induces oncogenesis and tumor development through IGF1 and Wnt axes.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 28;13(1):4364. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32119-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35902588 Free PMC article.
-
Quiescent Adult Neural Stem Cells: Developmental Origin and Regulatory Mechanisms.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Sep;40(9):1353-1363. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01206-1. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 38656419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patel D, Scott CS. Inhibitor studies of purified haemopoietic (myeloid) cell esterases. Evidence for the existence of distinct enzyme species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991;42(8):1577–85. Epub 1991/09/27. . - PubMed
-
- D'Amico M, Wu K, Fu M, Rao M, Albanese C, Russell RG, et al. The inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4a/alternative reading frame (INK4a/ARF) locus encoded proteins p16INK4a and p19ARF repress cyclin D1 transcription through distinct cis elements. Cancer Res. 2004;64(12):4122–30. Epub 2004/06/19. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2519 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

