Metformin Increases Proliferative Activity and Viability of Multipotent Stromal Stem Cells Isolated from Adipose Tissue Derived from Horses with Equine Metabolic Syndrome
- PMID: 30678275
- PMCID: PMC6406832
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020080
Metformin Increases Proliferative Activity and Viability of Multipotent Stromal Stem Cells Isolated from Adipose Tissue Derived from Horses with Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
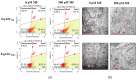
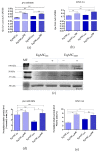
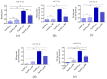
In this study, we investigated the influence of metformin (MF) on proliferation and viability of adipose-derived stromal cells isolated from horses (EqASCs). We determined the effect of metformin on cell metabolism in terms of mitochondrial metabolism and oxidative status. Our purpose was to evaluate the metformin effect on cells derived from healthy horses (EqASCHE) and individuals affected by equine metabolic syndrome (EqASCEMS). The cells were treated with 0.5 μM MF for 72 h. The proliferative activity was evaluated based on the measurement of BrdU incorporation during DNA synthesis, as well as population doubling time rate (PDT) and distribution of EqASCs in the cell cycle. The influence of metformin on EqASC viability was determined in relation to apoptosis profile, mitochondrial membrane potential, oxidative stress markers and BAX/BCL-2 mRNA ratio. Further, we were interested in possibility of metformin affecting the Wnt3a signalling pathway and, thus, we determined mRNA and protein level of WNT3A and β-catenin. Finally, using a two-tailed RT-qPCR method, we investigated the expression of miR-16-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-29a-3p, miR-140-3p and miR-145-5p. Obtained results indicate pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects of metformin on EqASCs. In this study, MF significantly improved proliferation of EqASCs, which manifested in increased synthesis of DNA and lowered PDT value. Additionally, metformin improved metabolism and viability of cells, which correlated with higher mitochondrial membrane potential, reduced apoptosis and increased WNT3A/β-catenin expression. Metformin modulates the miRNA expression differently in EqASCHE and EqASCEMS. Metformin may be used as a preconditioning agent which stimulates proliferative activity and viability of EqASCs.
Keywords: adipose-derived stromal cells; equine metabolic syndrome; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
M.K has shares in TATAA Biocenter. The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures





Similar articles
-
Orientin Reverses Premature Senescence in Equine Adipose Stromal Cells Affected by Equine Metabolic Syndrome Through Oxidative Stress Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 17;26(14):6867. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146867. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725115 Free PMC article.
-
The Haematococcus pluvialis extract enriched by bioaccumulation process with Mg(II) ions improves insulin resistance in equine adipose-derived stromal cells (EqASCs).Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Aug;116:108972. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108972. Epub 2019 May 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31103825
-
The Cladophora glomerata Enriched by Biosorption Process in Cr(III) Improves Viability, and Reduces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Equine Metabolic Syndrome Derived Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Stem Cells (ASCs) and Their Extracellular Vesicles (MV's).Mar Drugs. 2017 Dec 8;15(12):385. doi: 10.3390/md15120385. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29292726 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) Maintains Proper Equine Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells (ASCs)' Metabolic Functions and Negatively Regulates their Basal Adipogenic Potential.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Oct;19(7):2251-2273. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10580-8. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37402098 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin inhibits human breast cancer cell growth by promoting apoptosis via a ROS-independent pathway involving mitochondrial dysfunction: pivotal role of superoxide dismutase (SOD).Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Dec;41(6):637-650. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0398-0. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 30088260
Cited by
-
Zirconium Oxide Thin Films Obtained by Atomic Layer Deposition Technology Abolish the Anti-Osteogenic Effect Resulting from miR-21 Inhibition in the Pre-Osteoblastic MC3T3 Cell Line.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Mar 9;15:1595-1610. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S237898. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32210554 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Nanohydroxyapatite (nHAp)-Based Scaffold Doped with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IO), Functionalized with Small Non-Coding RNA (miR-21/124) Modulates Expression of Runt-Related Transcriptional Factor 2 and Osteopontin, Promoting Regeneration of Osteoporotic Bone in Bilateral Cranial Defects in a Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Model (SAM/P6). PART 2.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Aug 31;16:6049-6065. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S316240. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34511905 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Type 2 Diabetes Differently Impacts on the Select Functions of Bone Marrow-Derived Multipotent Stromal Cells.Cells. 2021 Jan 29;10(2):268. doi: 10.3390/cells10020268. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33572905 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin alleviates stress-induced cellular senescence of aging human adipose stromal cells and the ensuing adipocyte dysfunction.Elife. 2021 Sep 21;10:e62635. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62635. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34544550 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of stromal-like cells with CD207+/low CD1a+/low phenotype derived from histiocytic lesions - a perspective in vitro model for drug testing.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;24(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11807-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38342891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pagan J.D., Martin O.A., Crowley N.L. Relationship Between Body Condition and Metabolic Parameters in Sport Horses, Pony Hunters and Polo Ponies. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2009;29:418–420. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2009.04.117. - DOI
-
- Basinska K., Marycz K., Śmieszek A., Nicpoń J. The production and distribution of IL-6 and TNF-α in subcutaneous adipose tissue and their correlation with serum concentrations in Welsh ponies with equine metabolic syndrome. J. Vet. Sci. 2015;16:113–120. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.1.113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marycz K., Kornicka K., Basinska K., Czyrek A. Equine Metabolic Syndrome Affects Viability, Senescence, and Stress Factors of Equine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Stem Cells: New Insight into EqASCs Isolated from EMS Horses in the Context of Their Aging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016;2016:4710326. doi: 10.1155/2016/4710326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marycz K., Kornicka K., Grzesiak J., Śmieszek A., Szłapka J. Macroautophagy and Selective Mitophagy Ameliorate Chondrogenic Differentiation Potential in Adipose Stem Cells of Equine Metabolic Syndrome: New Findings in the Field of Progenitor Cells Differentiation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016;2016:3718468. doi: 10.1155/2016/3718468. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

