Plasma Peptidome Pattern of Breast Cancer Using Magnetic Beads-Based Plasma Fractionation and MALDI-TOF MS: A Case Control Study in Egypt
- PMID: 30678429
- PMCID: PMC6485569
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.1.175
Plasma Peptidome Pattern of Breast Cancer Using Magnetic Beads-Based Plasma Fractionation and MALDI-TOF MS: A Case Control Study in Egypt
Abstract
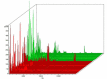
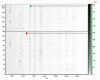
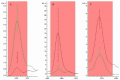
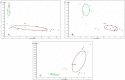
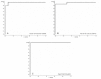
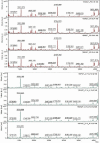
Objective: The present study aimed to determine peptidome patterns in breast cancer (BC). Methods: We analyzed the plasma proteomic profiling of 80 BC patients and 50 healthy controls, using hydrophobic interaction chromatography magnetic beads (MB-HIC8) separation followed by Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization/ time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Results: ClinProTools software identified 92 peaks that differed among the analyzed groups, 33 peaks were significantly different (P < 0.05). Of those, 22 peaks were up-regulated while 11 peaks were down-regulated in BC patients compared with the healthy controls. Three peptide ion signatures (m/z 1,570.31, 1,897.4 and 2,568.17) were provided by the Quick Classifier model to discriminate BC patients from healthy control subjects with 96.4% accuracy. External validation was performed by an independent group and this achieved a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 76.9%. Conclusion: MALDI-TOF MS has good analytical performance in distinguishing BC patients from healthy controls.
Keywords: Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization/ time of flight mass spectrometry; magnetic beads; ClinProTools.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
References
-
- Baralla A, Fois AG, Sotgiu E, et al. Plasma proteomic signatures in early chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2018;7:e1700088. - PubMed
-
- Baumann S, Ceglarek U, Fiedler GM, et al. Standardized approach to proteome profiling of human serum based on magnetic bead separation and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2005;51:973–80. - PubMed
-
- Calandra E, Posocco B, Crotti S, et al. Cross-validation of a mass spectrometric-based method for the therapeutic drug monitoring of irinotecan:implementation of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry in pharmacokinetic measurements. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:5369–77. - PubMed
-
- Callesen AK, Vach W, Jørgensen PE, et al. Reproducibility of mass spectrometry based protein profiles for diagnosis of breast cancer across clinical studies:a systematic review. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:1395–402. - PubMed
-
- De Noo ME, Mertens BJ, Ozalp A, et al. Detection of colorectal cancer using MALDI-TOF serum protein profiling. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:1068–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

