Antigen retrieval pre-treatment causes a different expression pattern of Cav3.2 in rat and mouse spinal dorsal horn
- PMID: 30678436
- PMCID: PMC6346256
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2019.2988
Antigen retrieval pre-treatment causes a different expression pattern of Cav3.2 in rat and mouse spinal dorsal horn
Abstract
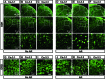
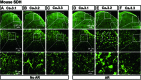
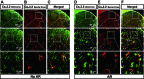
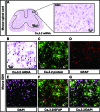
Cav3 channels consist of three isoforms, Cav3.1 (α1G), Cav3.2 (α1H), and Cav3.3 (α1I), which produce low-threshold spikes that trigger burst firings in nociceptive neurons of the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) and dorsal root ganglion (DRG). Although Cav3.2 plays a crucial role in pathological pain, its distribution in SDH still remains controversial. One study showed that Cav3.2 is ubiquitously expressed in neurons, but another study implied that Cav3.2 is expressed restricted to astrocytes. To unravel these discrepancies, we used methods of immunohistochemistry either with or without antigen retrieval (AR) pre-treatment to detect Cav3 in SDH and DRG from both rats and mice. Moreover, Cav3.2 mRNA was detected in mice SDH using in situ hybridization. We found that the expression pattern of Cav3.2 but not Cav3.1 and Cav3.3 in SDH were largely different with or without AR pre-treatment, which showed a neuron-like and an astrocyte-like appearance, respectively. Double staining further demonstrated that Cav3.2 was mainly co-stained with the neuronal marker NeuN in the presence of AR but was with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, marker for astrocytes) in the absence of AR pre-treatment. Importantly, Cav3.2 mRNA was mainly co-localized with Cav3.2 but not GFAP. Together, our findings indicate that AR pre-treatment or not impacts the expression pattern of Cav3.2, which may make a significant contribution to the future study of Cav3.2 in SDH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Perez-Reyes E. Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol Rev 2003;83:117-61. - PubMed
-
- Mckay BE, Mcrory JE, Molineux ML, Hamid J, Snutch TP, Zamponi GW, et al. CaV3 T-type calcium channel isoforms differentially distribute to somatic and dendritic compartments in rat central neurons. Eur J Neurosci 2006; 24:2581-94. - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Tsaur ML, Wang SW, Wang TY, Hung YC, Lin CS, et al. Chronic intrathecal infusion of mibefradil, ethosuximide and nickel attenuates nerve ligation-induced pain in rats. Br J Anaesth 2015;115:105-11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

