Current new challenges in the management of ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 30678445
- PMCID: PMC6361009
- DOI: 10.5217/ir.2018.00126
Current new challenges in the management of ulcerative colitis
Abstract
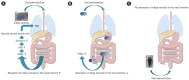
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract. Although the cause of UC is postulated to be multifactorial in nature, including genetic predisposition, epithelial barrier defects, dysregulation of immune responses, and environmental factors, the specific pathogenesis of UC is still incompletely understood. In the treatment of UC so far, a method of suppressing immunity and treating it has been mainstream. Immunosuppressant drugs, including thiopurines (azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine), anti-tumor necrosis factor-α (anti-TNF-α) antibody (infliximab and adalimumab), and calcineurin inhibitor, can be used in treat patients with corticosteroid-dependent and/or corticosteroid-refractory moderateto- severe UC. Recently, in addition to such a conventional therapeutic agent, golimumab, which is the first transgenic human monoclonal anti-TNF-α antibody to be fabricated, anti α-4/β-7 integrin antibody, and Janus kinase inhibitor have been reported to novel immunosuppressant therapy. Furthermore, other treatments with unique mechanisms different from immunosuppression, have also been suggested, including fecal microbiota transplantation and Indigo naturalis, which is a Chinese herbal medicine. We compared the features and efficacy of these new treatments. In this issue, the features and treatment options for these new treatments is reviewed.
Keywords: Colitis, ulcerative; Fecal microbiota transplantation; Indigo naturalis; Tofacitinib; Vedolizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Faubion WA, Jr, Loftus EV, Jr, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. The natural history of corticosteroid therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:255–260. - PubMed
-
- Palladino MA, Bahjat FR, Theodorakis EA, Moldawer LL. Anti-TNF-alpha therapies: the next generation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:736–746. - PubMed
-
- Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2462–2476. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

