The sleep-wake cycle regulates brain interstitial fluid tau in mice and CSF tau in humans
- PMID: 30679382
- PMCID: PMC6410369
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aav2546
The sleep-wake cycle regulates brain interstitial fluid tau in mice and CSF tau in humans
Abstract
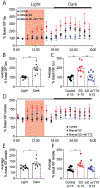
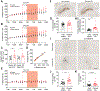
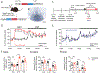
The sleep-wake cycle regulates interstitial fluid (ISF) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of β-amyloid (Aβ) that accumulates in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Furthermore, chronic sleep deprivation (SD) increases Aβ plaques. However, tau, not Aβ, accumulation appears to drive AD neurodegeneration. We tested whether ISF/CSF tau and tau seeding and spreading were influenced by the sleep-wake cycle and SD. Mouse ISF tau was increased ~90% during normal wakefulness versus sleep and ~100% during SD. Human CSF tau also increased more than 50% during SD. In a tau seeding-and-spreading model, chronic SD increased tau pathology spreading. Chemogenetically driven wakefulness in mice also significantly increased both ISF Aβ and tau. Thus, the sleep-wake cycle regulates ISF tau, and SD increases ISF and CSF tau as well as tau pathology spreading.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Sleep well to slow Alzheimer's progression?Science. 2019 Feb 22;363(6429):813-814. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw5583. Science. 2019. PMID: 30792288 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spillantini MG, Goedert M, Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet neurology 12, 609–622 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS073613/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS103161/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG047999/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS074969/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS105929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 NS089381/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002346/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K76 AG054863/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

