The Denominator problem: estimating the size of local populations of men-who-have-sex-with-men and rates of HIV and other STIs in Switzerland
- PMID: 30679393
- PMCID: PMC6585275
- DOI: 10.1136/sextrans-2017-053363
The Denominator problem: estimating the size of local populations of men-who-have-sex-with-men and rates of HIV and other STIs in Switzerland
Abstract
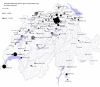
Objectives: There is no estimate of the current number of men who have sex with men (MSM) in Switzerland, or of their geographical distribution. We aimed to (1) estimate MSM concentration factors and population sizes for 83 Swiss postal code areas (PCA), including the nine largest Swiss cities, and (2) calculate MSM-specific local HIV prevalence and yearly rates of diagnosed HIV, hepatitis C virus (HCV), syphilis and gonorrhoea.
Methods: We triangulated data from general population estimates, MSM online surveys, published data on HIV prevalence and Swiss notification data for HIV and STDs. We compared two different formulae for the estimation of local MSM populations and calculated Bayesian 95%-credible-intervals (CrI) for each PCA.
Results: Across Switzerland, we estimate the MSM population aged 15-64 at roughly 80 000 men (95% CrI 64 000-96 000). (1) MSM in Switzerland were most concentrated in the five largest cities of Zurich, Geneva, Lausanne, Bern and Basel. (2) We estimate that in 2012, 6300 MSM, or 8.0%, were living with HIV, both diagnosed and undiagnosed and 1700 MSM, or 2.2%, had non-suppressed HIV infection. Between 2010 and 2013, average yearly rates of diagnosed HIV, HCV, syphilis and gonorrhoea were 0.3%, 0.02%, 0.4 % and 0.4 %, respectively.
Conclusions: Combining general population data, MSM online surveys and notification data allows the calculation of realistic estimates of local MSM populations and thus proportions of MSM with diagnosed HIV and other STIs, with implications for prevention planning, commissioning of health services and counselling MSM on HIV/STI risk. Our methodology for Switzerland is transferable to other countries with similar data sources.
Keywords: Bayes theorem; HCV; HIV infections; STD; homosexuality, male; incidence; prevalence; sexual and gender minorities.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Jeannin A, Meystre-Agustoni G, Lociciro S. Système de suivi de la stratégie de lutte contre le VIH/sida en Suisse : rapport de synthèse 2004-2008 [Monitoring system for the HIV/AIDS strategy in Switzerland. synthesis report 2004-2008]. Lausanne: Institut universitaire de médecine sociale et préventive (IUMSP). 2010. Available: https://serval.unil.ch/resource/serval:BIB_F8240BA3DE56.P001/REF
-
- Lociciro S, Simonson T, Samitca S, et al. . Système de surveillance du VIH et des IST de deuxième génération en Suisse. Rapport de synthèse 2012-2016 [Second-generation HIV and STI surveillance system in Switzerland. Synthesis report 2012-2016]. Lausanne: institut universitaire de médecine sociale et préventive (IUMSP). 2016. Available: https://www.iumsp.ch/Publications/pdf/rds278_fr.pdf
-
- Bajos N, Bozon M. Enquête sur la sexualité en France. Pratiques, Genre et Santé. Paris: [Sexuality in France. Practices, Gender and Health]Éditions La Découverte, 2008.
-
- Von Rüden U. Public Awareness of AIDS in the Federal Republic of Germany. Knowledge, attitudes and behaviour relating to protection against AIDS. A repeat survey by the Federal Centre for Health Education (BZgA). Cologne, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
