Learning from Longitudinal Data in Electronic Health Record and Genetic Data to Improve Cardiovascular Event Prediction
- PMID: 30679510
- PMCID: PMC6345960
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36745-x
Learning from Longitudinal Data in Electronic Health Record and Genetic Data to Improve Cardiovascular Event Prediction
Abstract
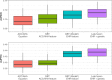
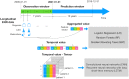
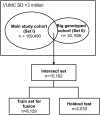
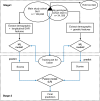
Current approaches to predicting a cardiovascular disease (CVD) event rely on conventional risk factors and cross-sectional data. In this study, we applied machine learning and deep learning models to 10-year CVD event prediction by using longitudinal electronic health record (EHR) and genetic data. Our study cohort included 109, 490 individuals. In the first experiment, we extracted aggregated and longitudinal features from EHR. We applied logistic regression, random forests, gradient boosting trees, convolutional neural networks (CNN) and recurrent neural networks with long short-term memory (LSTM) units. In the second experiment, we applied a late-fusion approach to incorporate genetic features. We compared the performance with approaches currently utilized in routine clinical practice - American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Pooled Cohort Risk Equation. Our results indicated that incorporating longitudinal feature lead to better event prediction. Combining genetic features through a late-fusion approach can further improve CVD prediction, underscoring the importance of integrating relevant genetic data whenever available.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO | The top 10 causes of death. WHO (2018). Available at: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM080178/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007450/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010685/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR064768/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133786/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM109145/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 18AMTG34280063/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 GM120523/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

