Search for efficient inhibitors of myotoxic activity induced by ophidian phospholipase A2-like proteins using functional, structural and bioinformatics approaches
- PMID: 30679550
- PMCID: PMC6346006
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36839-6
Search for efficient inhibitors of myotoxic activity induced by ophidian phospholipase A2-like proteins using functional, structural and bioinformatics approaches
Abstract
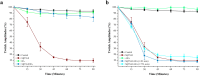
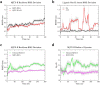
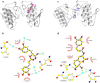
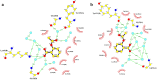
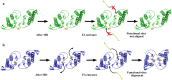
Ophidian accidents are considered an important neglected tropical disease by the World Health Organization. Particularly in Latin America, Bothrops snakes are responsible for the majority of the snakebite envenomings that are not efficiently treated by conventional serum therapy. Thus, the search for simple and efficient inhibitors to complement this therapy is a promising research area, and a combination of functional and structural assays have been used to test candidate ligands against specific ophidian venom compounds. Herein, we tested a commercial drug (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA) and a plant compound with antiophidian properties (rosmarinic acid, RA) using myographic, crystallographic and bioinformatics experiments with a phospholipase A2-like toxin, MjTX-II. MjTX-II/RA and MjTX-II/ASA crystal structures were solved at high resolution and revealed the presence of ligands bound to different regions of the toxin. However, in vitro myographic assays showed that only RA is able to prevent the myotoxic effects of MjTX-II. In agreement with functional results, molecular dynamics simulations showed that the RA molecule remains tightly bound to the toxin throughout the calculations, whereas ASA molecules tend to dissociate. This approach aids the design of effective inhibitors of PLA2-like toxins and, eventually, may complement serum therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
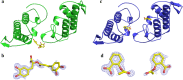
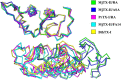
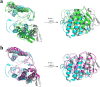
Similar articles
-
Structural and functional characterization of suramin-bound MjTX-I from Bothrops moojeni suggests a particular myotoxic mechanism.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 9;8(1):10317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28584-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29985425 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of phospholipase A2-like myotoxin inhibition by chicoric acid, a novel potent inhibitor of ophidian toxins.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Dec;1862(12):2728-2737. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 30251662
-
Crystal structure of a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper venom: Insights into a new putative "myotoxic cluster".Biochimie. 2017 Feb;133:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28034717
-
Crystallization of bothropstoxin II isolated from the venom of Bothrops jararacussu.Toxicon. 1996 May;34(5):614-7. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(95)00143-3. Toxicon. 1996. PMID: 8783457 Review.
-
An overview of lysine-49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins from crotalid snake venoms and their structural determinants of myotoxic action.Toxicon. 2003 Dec 15;42(8):885-901. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.008. Toxicon. 2003. PMID: 15019489 Review.
Cited by
-
The allosteric activation mechanism of a phospholipase A2-like toxin from Bothrops jararacussu venom: a dynamic description.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 1;10(1):16252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73134-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33004851 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Evaluation of Quercetin Methylated Derivatives on the Interaction with Secretory Phospholipases A2 from Crotalus durissus terrificus and Bothrops jararacussu.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 15;16(4):597. doi: 10.3390/ph16040597. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111354 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling polyphenol-protein interactions: a comprehensive computational analysis.J Cheminform. 2025 Apr 10;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13321-025-00997-3. J Cheminform. 2025. PMID: 40211304 Free PMC article.
-
Amplification of Snake Venom Toxicity by Endogenous Signaling Pathways.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jan 22;12(2):68. doi: 10.3390/toxins12020068. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Insights of Polyphenolic Compounds from Rosemary Bound to Their Protein Targets Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Free-Energy Calculations.Foods. 2023 Jan 14;12(2):408. doi: 10.3390/foods12020408. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673500 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

