Optical limiting properties of surface functionalized nanodiamonds probed by the Z-scan method
- PMID: 30679574
- PMCID: PMC6345928
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36838-7
Optical limiting properties of surface functionalized nanodiamonds probed by the Z-scan method
Abstract
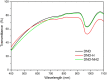
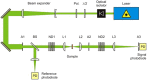
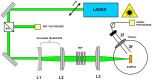
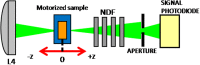
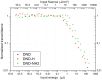
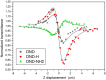
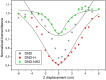
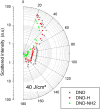
This work focuses on the optical limiting behavior of surface modified nanodiamonds (DNDs) namely, amino-terminated DNDs (DND-NH2) and hydrogen-terminated DNDs (DND-H). Their relevant nonlinear optical properties for optical limiting are compared to those of unfunctionalized DNDs. The optical limitation is characterized by means of nonlinear transmittance, Z-scan, and scattered intensity assessments when submitted to a nanosecond pulsed Nd:YAG laser operating at a wavelength of 532 nm. It is stated that the largest nonlinear attenuation is attributed to the DND-H system, whereas the exceedingly low threshold values for optical limiting for the DND-H and the DND-NH2 systems is attributed to their negative electron affinity character (NEA). Using Z-scan experiments, it is shown that nonlinear refraction combined with a significant nonlinear absorption predominates in the DND-H suspension, while the pure thermal origin of the nonlinear refractive index change is conjectured in the case of the DNDs. Besides, an amazing valley to peak profile was measured on DND - NH2indicating an unexpected positive sign of the nonlinear refraction coefficient. In addition, a stronger backscattered intensity signal is highlighted for the unfunctionalized DNDs through nonlinear scattering measurements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonlinear optical behavior of porphyrin functionalized nanodiamonds: an efficient material for optical power limiting.Appl Opt. 2016 May 10;55(14):3801-8. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.003801. Appl Opt. 2016. PMID: 27168296
-
Effect of Surface Chemistry on the Fluorescence of Detonation Nanodiamonds.ACS Nano. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):10924-10934. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b04647. Epub 2017 Nov 3. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 29088544
-
Optical properties of functionalized nanodiamonds.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 26;7(1):14086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14553-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29074983 Free PMC article.
-
Intensity-Dependent Optical Response of 2D LTMDs Suspensions: From Thermal to Electronic Nonlinearities.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;13(15):2267. doi: 10.3390/nano13152267. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon nanotube-based functional materials for optical limiting.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007 Apr-May;7(4-5):1268-83. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2007.308. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17450890 Review.
References
-
- Liu KK, Cheng CL, Chang CC, Chao JL. Biocompatible and detectable carboxylated nanodiamond on human cell. Nanotechnology. 2007;18(32):5102. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/18/32/325102. - DOI
-
- Volnova AB, Gordeev SK, Lenkov D. Targeted Delivery of 4-Aminopyridine Into the Rat Brain by Minicontainers from Carbon-Nanodiamonds Composite. Journal of Neuroscience and Neuroengineering. 2013;2(6):569–573. doi: 10.1166/jnsne.2013.1088. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

