The Impact of Cardiac Lipotoxicity on Cardiac Function and Mirnas Signature in Obese and Non-Obese Rats with Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 30679580
- PMCID: PMC6345821
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36914-y
The Impact of Cardiac Lipotoxicity on Cardiac Function and Mirnas Signature in Obese and Non-Obese Rats with Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
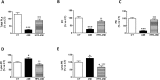
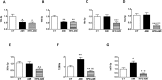
Cardiac lipotoxicity is involved in the cardiac functional consequences associated with obesity. Therefore, the aim of this study was to explore whether changes in the mitochondrial lipid cardiac profile could reflect differences in cardiac function and structure in obese and non-obese rats with myocardial infarction (MI). Whether these changes can also be reflected in a specific plasma miRNA signature as markers of cardiac damage was also evaluated. Rats were fed with either standard (3.5% fat) or high fat diet (35% fat) for 6 weeks before the induction of MI and sacrificed 4 weeks later. MI showed cardiac lipotoxicity independently of the presence of obesity, although obese and non-obese rats did not present the same cardiac lipid profile at mitochondrial level. Several cardiac lipid species in mitochondria, including cardiolipins and triglycerides, were associated with myocardial fibrosis, with mitochondrial triglyceride levels being independently associated with it; this supports that lipotoxicity can affect cardiac function. MI down-regulated plasma levels of miRNA 15b-5p and 194-5p in obese and non-obese animals, which were associated with cardiac function, mitochondrial lipids and myocardial fibrosis, with miRNA 15b-5p levels being independently associated with cardiac fibrosis. This could support that lipotoxicity could affect heart function by modulating plasma miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 deficiency facilitates myocardial dysfunction during high fat diet-induced obesity by promoting lipotoxicity and inflammation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Dec;1863(12):3128-3141. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28844956
-
MicroRNA Expression Signature Is Altered in the Cardiac Remodeling Induced by High Fat Diets.J Cell Physiol. 2016 Aug;231(8):1771-83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25280. Epub 2015 Dec 30. J Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26638879
-
The Crosstalk between Cardiac Lipotoxicity and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in the Cardiac Alterations in Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats.Cells. 2020 Feb 17;9(2):451. doi: 10.3390/cells9020451. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32079154 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6: A Potential Role in Cardiac Metabolic Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 21;19(9):2474. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092474. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30134607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of myocardial fibrosis by MicroRNAs.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010 Nov;56(5):454-9. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181ee81df. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20625314 Review.
Cited by
-
Prioritizing obesity treatment: expanding the role of cardiologists to improve cardiovascular health and outcomes.Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 7;12(1):e0279. doi: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000279. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36777095 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-glucose index trajectories and radiofrequency ablation outcomes in patients with stage 3D atrial fibrillation.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Apr 5;23(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02219-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38581024 Free PMC article.
-
The Cardiac Lipidome in Models of Cardiovascular Disease.Metabolites. 2020 Jun 17;10(6):254. doi: 10.3390/metabo10060254. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32560541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Promotes Cardiac Remodeling in Myocardial Infarction through the Activation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 23;11(7):1232. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071232. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883722 Free PMC article.
-
Right Heart Morphology and Its Association With Excessive and Deficient Cardiac Visceral Adipose Tissue.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2021 Sep 29;15:11795468211041330. doi: 10.1177/11795468211041330. eCollection 2021. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34602829 Free PMC article. Review.

