Phase 1 dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of eribulin-liposomal formulation in patients with solid tumours
- PMID: 30679780
- PMCID: PMC6461749
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0377-x
Phase 1 dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of eribulin-liposomal formulation in patients with solid tumours
Abstract
Background: This phase 1 study examined the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and preliminary efficacy of eribulin-liposomal formulation (eribulin-LF) in patients with advanced solid tumours.
Methods: Eligible patients with ECOG PS 0-1 were treated with eribulin-LF either on day 1 every 21 days (Schedule 1), or on days 1 and 15 every 28 days (Schedule 2). Doses ranged from 1.0 to 3.5 mg/m2, with dose escalation in a 3 + 3 design. The dose-expansion phase evaluated eribulin-LF in select tumour types.
Primary objectives: maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and the recommended dose/schedule of eribulin-LF.
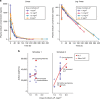
Results: Totally, 58 patients were enroled (median age = 62 years). The MTD was 1.4 mg/m2 (Schedule 1) or 1.5 mg/m2 (Schedule 2), the latter dose selected for the dose-expansion phase. Dose-limiting toxicity (DLTs) in Schedule 1: hypophosphatemia and increased transaminase levels. DLTs in Schedule 2: stomatitis, increased alanine aminotransferase, neutropenia and febrile neutropenia. The pharmacokinetic profile of eribulin-LF showed a similar half-life to that of eribulin (~30 h), but with a 5-fold greater maximum serum concentration and a 40-fold greater area-under-the-curve. Eribulin-LF demonstrated clinical activity with approximately 10% of patients in both schedules achieving partial responses.
Conclusions: Eribulin-LF was well tolerated with a favourable pharmacokinetic profile. Preliminary evidence of clinical activity in solid tumours was observed.
Conflict of interest statement
T.R.J.E.: honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Eisai; participated in speaker’s bureau for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai and Celgene; paid consultancy from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Celgene and Karus Therapeutics; received research funding from Astra Zeneca, Celgene, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Ono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lily, Basilea, Vertex, Merck, Daiichi Sankyo, Nutide, Sierra, Immunocore Verastem; expenses paid by Bristol-Myers Squibb; Subject Editor of the
Figures
References
-
- Kawano S, Asano M, Adachi Y, Matsui J. Antimitotic and non-mitotic effects of eribulin mesilate in soft tissue sarcoma. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1553–1561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

