Comprehensive analysis of potential prognostic genes for the construction of a competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30679912
- PMCID: PMC6338110
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S188913
Comprehensive analysis of potential prognostic genes for the construction of a competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an extremely common malignant tumor with worldwide prevalence. The aim of this study was to identify potential prognostic genes and construct a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulatory network to explore the mechanisms underlying the development of HCC.
Methods: Integrated analysis was used to identify potential prognostic genes in HCC with R software based on the GSE14520, GSE17548, GSE19665, GSE29721, GSE60502, and the Cancer Genome Atlas databases. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway-enrichment analyses were performed to explore the molecular mechanisms of potential prognostic genes. Differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) and lncRNAs (DELs) were screened based on the Cancer Genome Atlas database. An lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA regulatory network was constructed based on information about interactions derived from the miRcode, TargetScan, miRTarBase, and miRDB databases.
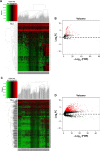
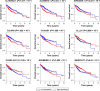
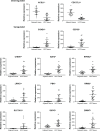
Results: A total of 152 potential prognostic genes were screened that were differentially expressed in HCC tissue and significantly associated with overall survival of HCC patients. There were 13 key potential prognostic genes in the ceRNA regulatory network: eleven upregulated genes (CCNB1, CEP55, CHEK1, EZH2, KPNA2, LRRC1, PBK, RRM2, SLC7A11, SUCO, and ZWINT) and two downregulated genes (ACSL1 and CDC37L1) whose expression might be regulated by eight DEMs and 61 DELs. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis showed that nine DELs (AL163952.1, AL359878.1, AP002478.1, C2orf48, C10orf91, CLLU1, CLRN1-AS1, ERVMER61-1, and WARS2-IT1) in the ceRNA regulatory network were significantly associated with HCC-patient prognoses.
Conclusion: This study identified potential prognostic genes and constructed an lncRNA- miRNA-mRNA ceRNA regulatory network of HCC, which not only has important clinical significance for early diagnoses but also provides effective targets for HCC treatments and could provide new insights for HCC-interventional strategies.
Keywords: ceRNA; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognostic gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Prognostic lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs Forming a Competing Endogenous RNA Network in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):1953-1967. doi: 10.1159/000492519. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30092571
-
Excavating novel diagnostic and prognostic long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and gene co-expression networks.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12821-12838. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2003925. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34898376 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Network in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 15;10:554759. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.554759. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33042838 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
The role of competing endogenous RNA network in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: potential therapeutic targets.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 31;12:1341999. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1341999. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38357004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma based on aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks and Cox regression models.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20191554. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191554. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31950990 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-malarial drug dihydroartemisinin downregulates the expression levels of CDK1 and CCNB1 in liver cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Sep;22(3):653. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12914. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34386075 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis proposes a possible role for long noncoding RNA MIR17HG in retinoblastoma.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Feb;7(2):e1933. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1933. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38321787 Free PMC article.
-
KPNA2-Associated Immune Analyses Highlight the Dysregulation and Prognostic Effects of GRB2, NRAS, and Their RNA-Binding Proteins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2020 Oct 26;11:593273. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.593273. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33193737 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an HCC recurrence model basedon the investigation of immune-relatedlncRNAs and related mechanisms.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 10;26:1387-1400. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.11.006. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34900397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

