The incidence of skin lesions in contrast media-induced chemical hypersensitivity
- PMID: 30679982
- PMCID: PMC6327547
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7056
The incidence of skin lesions in contrast media-induced chemical hypersensitivity
Abstract
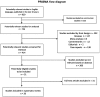
Contrast agents are used in radiology to increase the sensibility and specificity of radiological techniques. Some of these compounds have side effects that include organ toxicity (with kidney being the most affected organ) and hypersensitivity reactions. We performed multiple PubMed searches from January, 2008 to January, 2018 for studies regarding adverse reactions to compounds used as contrast agents in imagistic techniques. The initial research identified 929 records written in English. After further excluding 223 non-human studies, 292 articles that had irrelevant designs as reviews, meta-analysis, commentaries, editorials and case reports, 414 studies were selected for retrieval. After reading the abstracts, we excluded 363 studies as they had little relevance to the study. In total, 51 full-articles were assessed for eligible studies to be included. Finally, 20 articles were included in the analysis. In our systematic literature search the incidence of overall skin immediate reactions to iodinated contrast media (ICM) had an incidence between 1.15 and 0.12%, depending on the cohort analyzed in the studies. The percentage of cutaneous manifestations in the cohort that experienced immediate hypersensitivity reactions was between 33.33 and 87.7%. The most frequent skin manifestations were urticaria, rashes, pruritus and limited facial edema. Non-iodinated contrast agents have a safer profile compared with ICM, the incidence of immediate adverse reactions being very low in gadolinium-based contrast agents and other agents used for contrast-enhanced ultrasound. The incidence of delayed reactions was between 10.1 and 0.03%. In the studies analyzed by us the main adverse reactions due to delayed hypersensitivity phenomena were cutaneous manifestations that were present between 70.27 and 100% of the cases. Regarding the risk factors for developing immediate adverse reactions, being female was a predisposing factor accompanied by history of allergy and history of reactions to contrast media. An accurate anamnesis of the patients and a correctly conducted pretreatment can limit the incidence and the severity of the adverse reactions and also can avoid the life occurrence of life-threatening reactions.
Keywords: contrast agents; delayed hypersensitivity reactions; gadolinium-based contrast agents; immediate hypersensitivity reactions; iodinated contrast agents.
Figures
References
-
- Filler A. The History, development and impact of computed imaging in neurological diagnosis and neurosurgery: CT, MRI, and DTI. https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3267 Nat Preced. 2009;7:1–76.
-
- Hasegawa M, Gomi T. Radiological contrast agents and radiopharmaceuticals. In: Ray SD, editor. Side Effects of Drugs Annual. 1st. Vol. 37. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2015. pp. 583–593. - DOI
-
- Mamoulakis C, Tsarouhas K, Fragkiadoulaki I, Heretis I, Wilks MF, Spandidos DA, Tsitsimpikou C, Tsatsakis A. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Basic concepts, pathophysiological implications and prevention strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;180:99–112. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.06.009. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources