Effects of paclitaxel intervention on pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 30679989
- PMCID: PMC6327549
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7045
Effects of paclitaxel intervention on pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
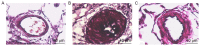
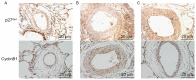
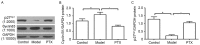
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of paclitaxel (PTX), at a non-cytotoxic concentration, on pulmonary vascular remodeling (PVR) in rats with pulmonary hypertension (PAH), and to explore the mechanisms underlying the PTX-mediated reversal of PVR in PAH. A total of 36 rats were divided into control group (n=12), model group (n=12) receiving a subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg) in the back on day 7 following left pneumonectomy and PTX group (n=12) with PTX (2 mg/kg) injection via the caudal vein 3 weeks following establishing the model. The degree of PVR among all groups, as well as the expression levels of Ki67, p27Kip1 and cyclin B1, were compared. The mean pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy index [right ventricle/(left ventricle + septum) ratio] and the thickness of the pulmonary arterial tunica media in the model group were 58.34±2.01 mmHg, 0.64±0.046 and 65.3±3.3%, respectively, which were significantly higher when compared with 23.30±1.14 mmHg, 0.32±0.028 and 16.2±1.3% in the control group, respectively (P<0.01). The mean pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy index and thickness of the pulmonary arterial tunica media in the PTX group were 42.35±1.53 mmHg, 0.44±0.029 and 40.5±2.6%, respectively, which were significantly lower when compared with the model group (P<0.01). Compared with the control group, the expression levels of Ki67 and cyclin B1 in the model group were significantly increased (P<0.01), while p27Kip1 expression was significantly reduced (P<0.01). Following PTX intervention, the expression levels of Ki67 and cyclin B1 were significantly reduced when compared with the model group (P<0.01), while p27Kip1 expression was significantly increased (P<0.01). The results of the present study suggest that PTX, administered at a non-cytotoxic concentration, may reduce PAH in rats, and prevent the effects of PVR in PAH. These effects of PTX may be associated with increased expression of p27Kip1 and decreased expression of cyclin B1.
Keywords: cell cycle; paclitaxel; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Figures

References
-
- Satoh T. Current practice for pulmonary hypertension. Chin Med J (Engl) 2014;127:3491–3195. - PubMed
-
- Ball MK, Waypa GB, Mungai PT, Nielsen JM, Czech L, Dudley VJ, Beussink L, Dettman RW, Berkelhamer SK, Steinhorn RH, et al. Regulation of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by vascular smooth muscle hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:314–324. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201302-0302OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
