Potential role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in delayed cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
- PMID: 30680005
- PMCID: PMC6327579
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7073
Potential role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in delayed cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
Abstract
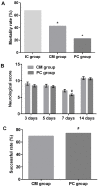
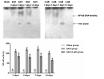
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) serves a key role in several neurological disorders, however, the specific role of PARP in delayed cerebral vasospasm (DCVS) following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) remains unclear. The present study was conducted to clarify the possible mechanism of PARP in DCVS with the treatment of 3-aminobenzamide (3-AB), a PARP inhibitor. In the preliminary experiment, an internal carotid artery puncture SAH model, a cisterna magna double injection SAH model and prechiasmatic cistern single injection SAH model were compared with respect to mortality and neurobehavioral test results. The prechiasmatic cistern single injection SAH model was chosen to induce DCVS in the formal experiment. In the formal experiment, a total of 96 Sprague Dawley rats were randomly allocated into the sham group, the SAH group and the SAH+3-AB group and then each group was further subdivided into days 3, 5, 7 and 14 post-SAH subgroups (n=8 for each subgroup). The prechiasmatic cistern single injection SAH model was established to induce DCVS. Neurobehavioral testing and HE staining were conducted to evaluate the degree of cerebral vasospasm. PARP activity was assessed by ELISA and immunohistochemistry. An electrophoretic mobility shift assay was used to detect nuclear factor (NF)-κB DNA-binding activity. The expression of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured by western blotting. Cerebral vasospasm occurred following SAH and became most severe on around day 7 post-SAH. NF-κB activity, PARP activity, the expression of MCP-1 and CRP exhibited a similar time course to cerebral vasospasm. Treatment with 3-AB alleviated the degree of cerebral vasospasm. NF-κB activity, PARP activity and the expression of MCP-1 and CRP were also suppressed by 3-AB treatment. In conclusion, PARP may serve an important role in regulating the inflammatory response and ultimately contribute to DCVS. Therefore 3-AB may be a potential therapeutic agent for DCVS.
Keywords: 3-AB; delayed cerebral vasospasm; inflammatory response; nuclear factor-κB; poly ADP-ribose polymerase; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Figures




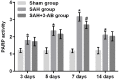

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase attenuates cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits.Stroke. 2001 Jan;32(1):225-31. doi: 10.1161/01.str.32.1.225. Stroke. 2001. PMID: 11136941
-
Alterations of caveolin-1 expression in a mouse model of delayed cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Oct;12(4):1993-2002. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3568. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27703494 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of simvastatin and taurine on delayed cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Apr;11(4):1355-1360. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3082. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27073449 Free PMC article.
-
PARP inhibition attenuates early brain injury through NF-κB/MMP-9 pathway in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage.Brain Res. 2016 Aug 1;1644:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 6. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27157545
-
In vivo animal models of cerebral vasospasm: a review.Neurosurgery. 2000 Feb;46(2):448-60; discussion 460-1. Neurosurgery. 2000. PMID: 10690735 Review.
Cited by
-
Activated protein C overexpression suppresses the pyroptosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage model cells by regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Dec;22(6):1391. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10827. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34650639 Free PMC article.
-
Modes of Brain Cell Death Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;16:799753. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.799753. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of Serum MicroRNA after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Aged Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 8;11(3):822. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030822. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979801 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and ACE Inhibitory Activity of Fermented Milk with Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum K25 as Analyzed by GC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 28;30(6):903-911. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1911.11007. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32160695 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
