Effects of liver function, insulin resistance and inflammatory factors on vascular endothelial dilation function and prognosis of coronary heart disease patients complicated with NAFLD
- PMID: 30680007
- PMCID: PMC6327639
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.7043
Effects of liver function, insulin resistance and inflammatory factors on vascular endothelial dilation function and prognosis of coronary heart disease patients complicated with NAFLD
Abstract
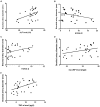
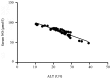
Effects of liver function, insulin resistance (IR) and inflammatory factors on vascular endothelial dilation function and prognosis of coronary heart disease (CHD) patients complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were investigated. A total of 80 patients with CHD treated in Jinan Central Hospital from October 2016 to July 2017 were randomly enrolled and divided into the NAFLD group (n=41) and the simple CHD group (n=39). The IR, the vascular endothelial dilation function and the related inflammatory factors were also detected, followed by statistical analysis. The level of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), serum total bilirubin and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels and body mass index in the NAFLD group was decreased and the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α was increased compared with that in the simple CHD group (P<0.05). There was a linearly positive correlation between ALT and brachial artery diameter in the NAFLD group (r=0.311, P<0.05). There was a correlation between homeostasis model assessment-IR (HOMA-IR) and HOMA-β indexes and brachial artery diameter, hs-CRP and brachial artery diameter in both groups (r=-0.128, r=0.219, P<0.05). The HOMA indexes in the NAFLD group were increased compared with those in the simple CHD group (P<0.01). There were significant differences in the intima-media thickness, number of carotid plaques and detection rate of carotid plaques (P<0.05). The risk of cardiovascular events within 10 years in the NAFLD group was increased compared with that in the simple CHD group. The differences of incidence of cardiovascular diseases (CVD)s were statistically significant (P<0.05). Therefore, The changes in liver function indexes, IR and related inflammatory factors in CHD patients complicated with NAFLD significantly affect the vascular endothelial dilation function, which also have some effects on the occurrence of CVDs.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; inflammatory factors; insulin resistance; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A study of the correlation of insulin resistance and leptin with inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial injury in T2DM patients with CHD.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):265-269. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6170. Epub 2018 May 16. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29896248 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of blood glucose, serum chemerin and insulin resistance with NAFLD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Mar;15(3):2936-2940. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5753. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29456698 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation analysis of gut microbiota and biochemical indexes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2019 May 20;27(5):369-375. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.05.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31177662 Chinese.
-
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome-Position Paper of the Indian National Association for the Study of the Liver, Endocrine Society of India, Indian College of Cardiology and Indian Society of Gastroenterology.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015 Mar;5(1):51-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25941433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coronary heart disease.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Oct 26;8(20):4688-4699. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i20.4688. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33195636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of Danhong injection on endothelial function and inflammatory factors after the percutaneous coronary intervention for coronary heart disease: A protocol of systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 2;99(27):e20783. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020783. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32629660 Free PMC article.
-
Increased cardiovascular events and mortality in females with NAFLD: a meta-analysis.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Aug 15;10(3):258-271. eCollection 2020. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32923108 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Gut Microbiome and Serum Metabolome in Coronary Artery Disease Patients Complicated With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Are Associated With Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jan 3;8:805812. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.805812. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35047580 Free PMC article.
-
Association of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in Asian Indians: A cross-sectional study.J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Jan 28;9(1):390-394. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_887_19. eCollection 2020 Jan. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020. PMID: 32110624 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of resveratrol supplementation on serum concentrations of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, fibroblast growth factor 21, and adiponectin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.BMC Nutr. 2025 Feb 10;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40795-025-00997-4. BMC Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39930480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szczepaniak LS, Babcock EE, Schick F, Dobbins RL, Garg A, Burns DK, McGarry JD, Stein DT. Measurement of intracellular triglyceride stores by H spectroscopy: validation in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:E977–E989. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, Charlton M, Sanyal AJ. American Gastroenterological Association; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; American College of Gastroenterologyh: The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:1592–1609. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fracanzani AL, Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Andreoletti M, Colli A, Vanni E, Bertelli C, Fatta E, Bignamini D, Marchesini G, et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels: a role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology. 2008;48:792–798. doi: 10.1002/hep.22429. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
